Class Variables
- Java has no CONSTANT declaration so......
// public - accessible from entire app
// static - class var
// final - value can't be changed
IN Olive()...
public static final long BLACK= 0x000000;
using it
public long color = Olive.BLACK;

Inheritance
- Java has only single inheritance - only one inherited parent
- Parent/child
- Base/derived
- Superclass/subclass <- Preferred Java nomenclature
- By default Object() is the superclass unless directly specified
Polymorphism
- Can used as Superclass or Subclass
- Declare the object by Superclass
Superclass can have more than one subclass
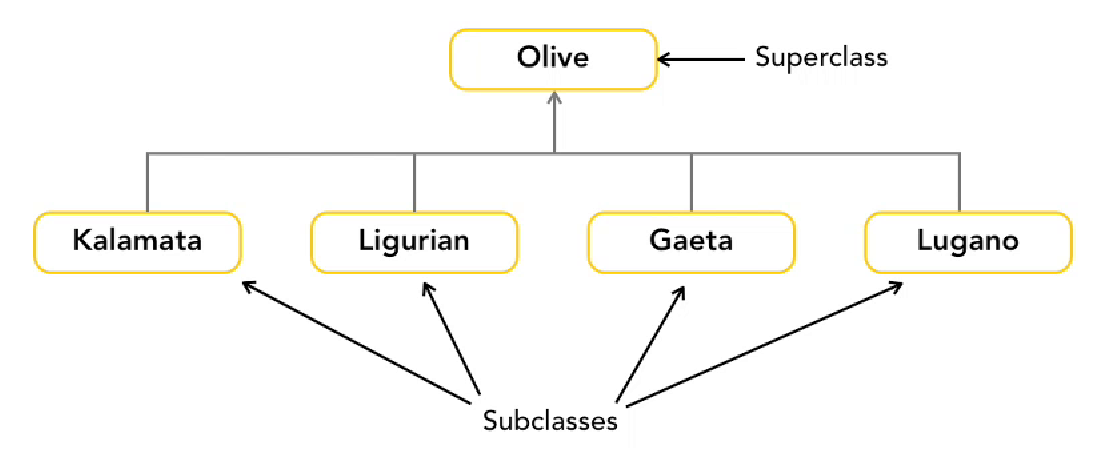
- Private - only called within own class
- Protected - called by own class or subclass
- Public - called from anywhere
Subclasses extend superclass
extending Olive by setting inital volume (setVolume)
public class Kalamata extends Olive() {
public Kalamata() {this.setVolume(2);}
}
public class Liguria extends Olive() {
public Liguria () {this.setVolume(5);}
}
…..this creates inheritance
Olive[] olives = {new Kalamata(), new Liguria(), new Kalamata()};
OlivePress press = new OlivePress(olives);
OliveOil oil - press.getOil;
Takes Kalamata() class and fits into Superclass Olive()
Extending Custom Classes
- Superclass doesnot pass on its constructor so...
- Each subclass needs its own constructor
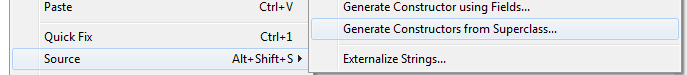
In subclass... use IDE to copy constructors from the Superclass
Can select all or one...
Superclass Olive() has two constructor methods (its overloaded)
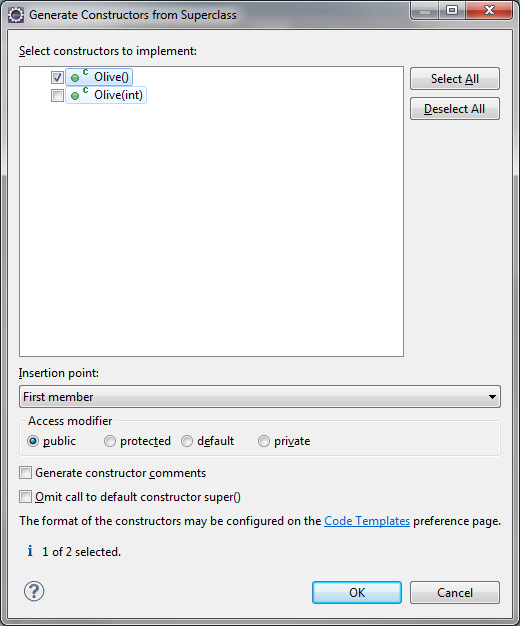
Creates...
public Kalamata() {
super();//calling superclass constructor method
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
Code: Main
package com.lynda.olivepress;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import com.lynda.olivepress.olives.Kalamata;
import com.lynda.olivepress.olives.Ligurian;
import com.lynda.olivepress.olives.Olive;
import com.lynda.olivepress.press.OlivePress;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Olive> olives = new ArrayList<Olive>();
Olive olive;
//olive = new Olive(2); //Was calling SuperClass
olive = new Kalamata();
System.out.println(olive.name);
olives.add(olive);
olive = new Ligurian();
System.out.println(olive.name);
olives.add(olive);
olive = new Kalamata();
System.out.println(olive.name);
olives.add(olive);
OlivePress press = new OlivePress();
press.getOil(olives);
System.out.println("You got " + press.getTotalOil() +
" units of oil");
press.getOil(olives);
System.out.println("You got " + press.getTotalOil() +
" units of oil");
}
}
Code:Olive.java
package com.lynda.olivepress.olives;
public class Olive {
public static final long BLACK = 0x000000;
public static final long GREEN = 0x00ff00;
public String name = "Kalamata";
public String flavor = "Grassy";
public long color = Olive.BLACK;
private int oil = 3;
public int getOil() {
return oil;
}
public void setOil(int oil) {
this.oil = oil;
}
public Olive() {
System.out.println("Constructor of " + this.name);
}
public Olive(int oil) {
setOil(oil);
}
public int crush() {
System.out.println("ouch!");
return oil;
}
}
Code:Kalamata
package com.lynda.olivepress.olives;
public class Kalamata extends Olive {
public Kalamata() {
super(2); //calling superclass constructor method and passing '2'
this.name = "Kalamata";
this.flavor = "Grassy";
this.color = Olive.BLACK;
}
}
- Log in to post comments
