Methods
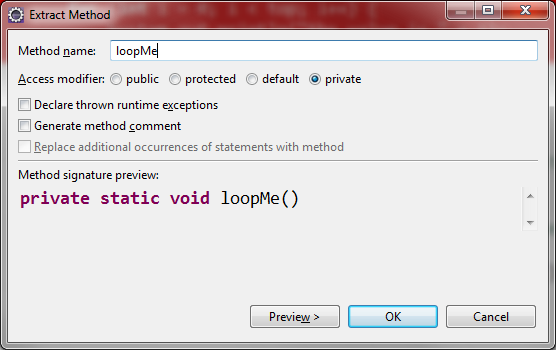
Refactoring
Code:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
doSomething();
//refactoring, copy code, Refactor..
//will create a new method and reference it here
loopMe();
}
private static void loopMe() {
int top = 10;
for (int i = 0; i < top; i++) {
System.out.println("the value is " + i);
}
}
//Access modifier public, private, protected (inheritance), none (protected package)
//Static - class method, only used inside class
//non-Static - used in instances
//Static must create instance to call non-Static '.method()'
private static void doSomething() {
System.out.println("This method has been called");
}
}

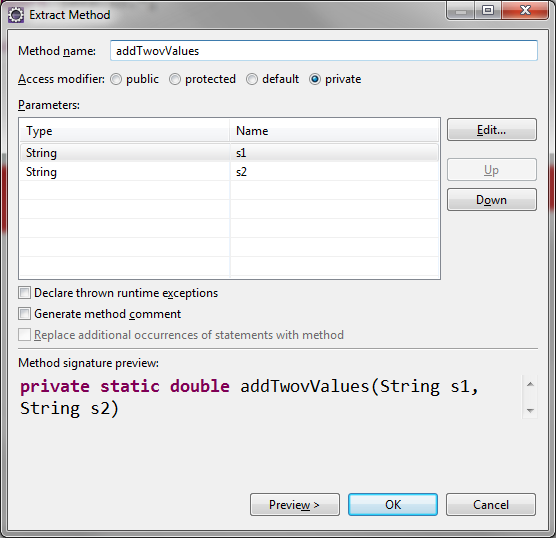
Extracting a Method
Code:
import java.io.*;
public class Calculator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = getInput("Enter a numeric value: ");
String s2 = getInput("Enter a numeric value: ");
// Extracting a Method
double result = addTwovValues(s1, s2);
System.out.println("The answer is " + result);
}
// Extracted Method
private static double addTwovValues(String s1, String s2) {
double d1 = Double.parseDouble(s1);
double d2 = Double.parseDouble(s2);
double result = d1 + d2;
return result;
}
private static String getInput(String prompt) {
BufferedReader stdin = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(System.in));
System.out.print(prompt);
System.out.flush();
try {
return stdin.readLine();
} catch (Exception e) {
return "Error: " + e.getMessage();
}
}
}

Method Overloading (Multiple methods with same name/diff args)
Code:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int value1 = 5;
int value2 = 10;
int value3 = 15;
int result = addValues(value1, value2, value3);
System.out.println("The result is: " + result);
String string1 = "10";
String string2 = "25";
int result2 = addValues(string1, string2);
System.out.println("The result is: " + result2);
}
private static int addValues(int int1, int int2){
return int1 + int2;
}
// will handle call if 3 values passed
private static int addValues(int int1, int int2, int int3){
return int1 + int2 + int3;
}
// handle different data types
private static int addValues(String val1, String val2){
int value1 = Integer.parseInt(val1);
int value2 = Integer.parseInt(val2);
return value1 + value2;
}
}
- Log in to post comments
