Passing By Copy; Primitives
When calling a function, a COPY of the argument is passed to the method
void incrementValue(int inFunction) {
inFunction ++;
System.out.println("In function: " + inFunction);
}
int original = 10;
System.out.println("Original before : " + original);
incrementValue(original);
System.out.println("Original after : " + original);
// Original before: 10
// In function: 11
// Original after: 10
}

Passing by Reference: Complex Objects
- Variable of Complex Object is a Reference to Memory
- A Copy of the Complex Object is passed, but references the same memory addresses
inf[] original = {10,20,30};
original[0] > {10,20,30} < inFunction[0]
Passing Strings: Is Complex Object but Acts Like Primitive
void changeString(String inFunction) {
inFunction = “New!”;
System.out.println(“In function: “ + inFunction);
}
- Strings are immutable, can’t change after declaration
- Copy of entire string passed to function
// Original before: Original!
// In function: New!
// Original after: Original!

Extract Method with Error Handling
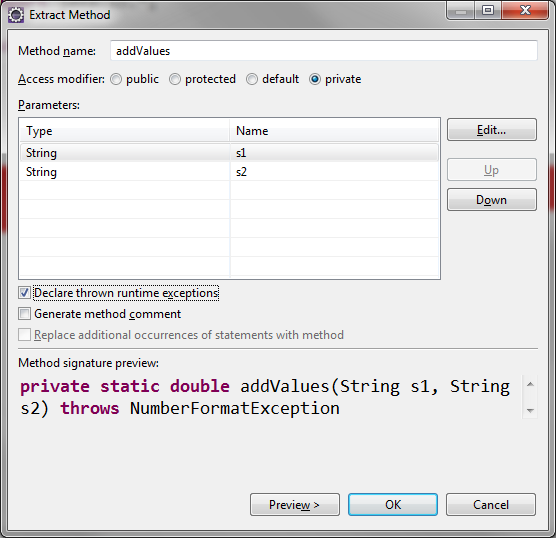

More Complex Programs and An Error Handling Declaration
Code:
import java.io.*;
public class Calculator2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = getInput("Enter a numeric value: ");
String s2 = getInput("Enter a numeric value: ");
String op = getInput("Enter 1=Add, 2=Subtract, 3=Multiply, 4=Divide: ");
int opInt = Integer.parseInt(op);
// declare variables BEFORE switch
double result = 0;
switch (opInt) {
case 1:
result = addValues(s1, s2);
break;
case 2:
result = subtractValues(s1, s2);
break;
case 3:
result = multiplyValues(s1, s2);
break;
case 4:
result = divideValues(s1, s2);
break;
default:
System.out.println("Unknown Operation: " + op);
break;
}
System.out.println("The answer is " + result);
}
private static double divideValues(String s1, String s2) {
double d1 = Double.parseDouble(s1);
double d2 = Double.parseDouble(s2);
double result = d1 / d2;
return result;
}
private static double multiplyValues(String s1, String s2) {
double d1 = Double.parseDouble(s1);
double d2 = Double.parseDouble(s2);
double result = d1 * d2;
return result;
}
private static double subtractValues(String s1, String s2) {
double d1 = Double.parseDouble(s1);
double d2 = Double.parseDouble(s2);
double result = d1 - d2;
return result;
}
private static double addValues(String s1, String s2)
throws NumberFormatException {
double d1 = Double.parseDouble(s1);
double d2 = Double.parseDouble(s2);
double result = d1 + d2;
return result;
}
private static String getInput(String prompt) {
BufferedReader stdin = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(System.in));
System.out.print(prompt);
System.out.flush();
try {
return stdin.readLine();
} catch (Exception e) {
return "Error: " + e.getMessage();
}
}
}
- Log in to post comments
