Main Class
public static void main(String[] args) {
Required by Class:
- public - can be called anywhere
- static - no instance required to run
- void - nothing returned by class
- String[] args
- [] - an array
- args - default variable to hold passed data
- Passed by Java’s JVM
Passing Args
Command Line
java Main arg1 arg2
In Eclipse:
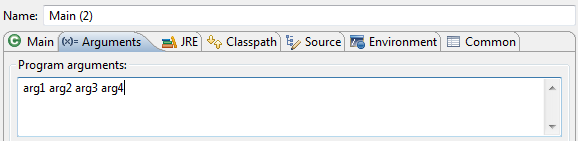
Documentation
- http://docs.oracle.com/javase/6/docs/api/
- Mouseover, F2
- Windows > View > Help
Garbage Collection
- Objects referenced created in heap memory
- As long as variable referenced, it’s retained
- When referenced expire, they’re eligible to be garbage collected
- Garbage Collector runs own thread
- Can’t force garbage collection
- OutOfMemoryError thrown if memory runs out
Expiration
- Variable to local functions or blocks expire when function is complete
- Set value to null
Tips for Managing Memory
- Minimize number of object created
- Runtime.*
- Runtime.maxMemory()
- Runtime.totalMemory()
- Runtime.freeMemory()
- java -Xms256s HelloWorld - Initial heap size
- java -Xms256m HelloWorld - Max heap size
- java -Xms256n HelloWorld - Heap size for young generation objects
Classes and Objects
//Starting class has main() method
public class SimpleApplication {
//
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Welcomer = datatype
// welcomer is new instance
Welcomer welcomer = new Welcomer();
welcomer.sayHello();
}
}
public class Welcomer {
// instance variable = welcome - private to the class
private String welcome = “Hello”;
public void sayHello() {
System.out.println(welcome);
}
}
String variables objects
String is class
String welcome = “Hello!”;
String welcome = new String(“Hello!”);
String = array[H,e,l,l,o,!]
Same as:
char[] chars = {‘H’,’e’,’l’,’l’,’o’,’!’};
String s = new String(chars);
Types of Variables
- Primitives - stored directly in memory
- Numerics - ints, floating point decimals
- Single characters
- Boolean (true/false)
- Complex objects
- Strings
- Dates
- Everything else
Declaring a Primitive Varialbe
- Data Type - Required
- Variable name - Required
- Initial value - option
- int newVariable = 10;
- [Data type] [Variable name] = [Initial value];
- variable name MUST start with lowercase
- Numeric default = 0
- Boolean default = false
Declaring a Complex Variable
- instance of classes
- declared in 3 parts
- Init uses new keyword and class constructor
- Inital value - optional, built from class constructor
- Date newDate = new Date();
- [Data type] [Variable name] = [Initial value from constructor]
- Variable name alpha char or _
- Date newDate = null
Scope
- local vars - declared inside function (de-referenced)
- void doSomething()
- public vars -
- public doSomethingElse()
Class variables = Field variable
- Declared outside a class method
public class MyClass {
String sayHello = new String(“Hello”);
void doSomething() {
System.out.println(sayHello);
}
}
- Log in to post comments
