Definitions
- SAN – Storage Area Network
- NAS – Network Attached Storage
- DAS – Direct Attached Storage
- SCSI – Small Computer Storage Interconnect (Interface?)
- FC – Fiber Channel Protocol
- FC – Fibre Channel light pipe cabling
- iSCSI – IP based SCSI communication
- TCP – Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol
- LAN – Local Area Network
- ROI – Return on Investment
- TCO – Total Cost of Ownership
- PBP – Pay Bay Period
- CDP – Continuous Data Protection
- IB – Infiniband
- Backup window – time it takes to back up data
- Server Clustering – method of making two or more servers appear as one
- DNS – Domain Name Servers
- WINS – Windows Internet Naming Servers
- DC – Domain Controllers
- HBA – Host Bus Adapter
- GBIC – Gigabit Interface Controller
- RAID – Redundant Array of Inexpensive (Independent) Disks
- JBOD – Just a Bunch Of Disks
- Storage Array – hardware/firmware combo
- Storage Network Industry Alliance
- GLM – Gigabit Link Module
- SAS – Serial Attached SCSI
- SATA – Serial ATA
- Layers
- Physical Layers
- Software Layers
- Protocol stack
- TCP/IP v.s. FC
- TCP/IP protocol with Ethernet (Files)
- FC protocol with FC Switches (Data)
- Functions
- LAN – move files
- SAN – direct access to hardware
- 4 P’s
- Parts
- Protocols
- Players
- Platforms
- Parts
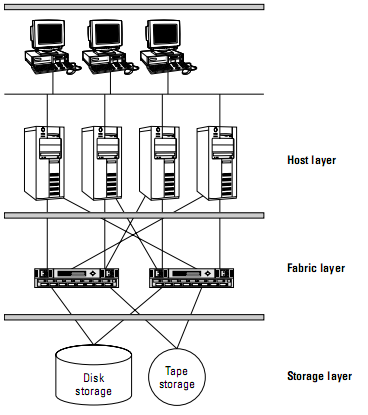
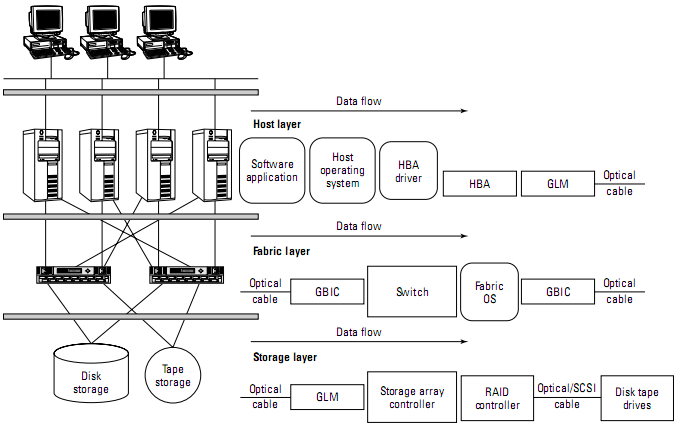
- Host Layer/Fabric Layer/Storage Layer
- Host Layer
- HBA – Host Bus Adapter
- Plugs into server itself
- Interfaces between software and hardware
- Gigabit Interface Controller
- This port is present at EVERY connection point in the FC network
- Houses laster and electronics that convert data from/to light/electronic pulses
- Interfaces between FC protocol and HBA for block access
- Fiber Optic Cable
- Used as interconnect
- 3 types, based on wavelength employed in the FC network
- Fabric Layer
- Middle layer of a SAN
- Hub
- (only one devices talks at a time) creates loop, thus SAN loop
- Switch
- Smart device that routes information to SPECIFIC destination
- Gateway/Bridge
- Converts data to/from differing protocols
- iSCSI to FC
- Router
- Moves data from separate networks
- Storage Layer
- All data exists here
- Disk drives, Tape drives, optical storage
- RAID/JBOD arrays
- Storage Array – big box of disks running smart code(firmware) for managing disks
- Modular
- Smaller unit with computer memory for caching data from slower disks
- Fewer port connections
- Upgrade via
- Shelves of 10-16 disks
- Plug-in controllers for more throughput
- Controllers usually are mirrored and have 16-32G memory
- Monolithic
- Huge machine with 100s of Gigs of memory
- Many port connections
- Hundreds of disks
- Shared GLOBAL memory
- SAN Protocols
- Fibre Channel
- Low-level protocol between disks and host applications
- FC-AL (Fibre Channel – Arbitrated Loop) [HUBS]
- FC-SW (Fibre Channel – Switched ) [SWITCHES]
- Fibre Channel provides a pipe for SCSI to work within
- SCSI
- Works on top of FC
- iSCSI over IP
- Infiniband iSER and SRP
- Platforms
- Olders OS’s such as Windows NT don’t support SAN
- Big, fast servers with Intel/AMD do
- Unix machines
- Mainframes
SAN Building Blocks
- Host Layer
- HBA
- HBA Drivers
- GBIC
- Cables
- Host Bus Adapter
- Hardware and BIOS firmware that works between OS and Disks
- GBICs and GLMs
- Shortwave
- .5 meters and 500 meters
- 780 nm and 850 nm
- Longwave
- 2m to 10km
- 1300nm and
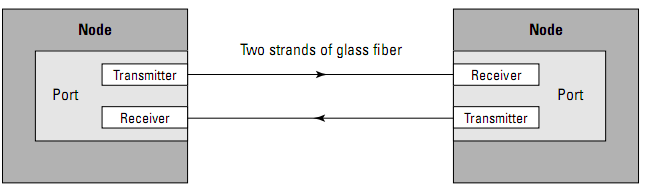
- Each GLM has 2 connections, IN and OUT (FULL DUPLEX)
- Full Duplex allows for simultaneous comm IN/OUT
- Each FC cable has 2 thin pieces of glass for this purpose
- SC
- Original connectors used in SANs
- 1Gps
- LC
- Smaller 2nd generation
- 2,4,8,10Gps
- Fabric Layer
- Fabric Layer – hardware in SAN, specifically FC components
- Storage Fabric – set of organized, connected storage devices on a network of interconnected switches that can be accessed by servers (up to 239)
- Switched Fabric – consists of all switches in a single storage fabric
- SAN Fabric – consists of all the individual switched fabrics in the SAN
- SANs can have more than one SAN fabric
- Usually two are present for redundancy
- When switches are not connected together, they constitute individual fabrics each with their own fabric ID in each switch
- - -
SAN v1.01.docx 4/8/2011 of
- Log in to post comments