Solution & Project Organization
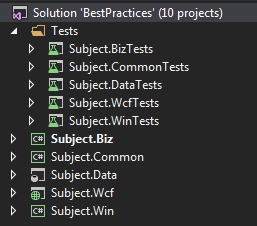
UI Layer
- Subject.Win
- Subject.Wpf
- Subject.Web
Business Logic Layer
- Subject.Biz
Data Layer
- Subject.Data > Database
- Utilities/Other
- Subject.Common
HTML Documentation
///<summary> ///Will return title ///</summary> ///<returns> </returns>
Class Fields & Properties
- Always make FIELDS private & if needed use PROPERTIES with get/set to expose to outside class
- Fields = Backend Fields
- propfull<TAB>
Fields should be camelCase
private string carType;
Properties should be PascalCase
public string CarType;
To expose a Field as a Property use 'Lazy Loading'
private string carType;
public string CarType
{
get{ return carType; }
set {carType = value; }
}
Methods
Tips
- Methods always verbs, never nouns
- Should reflect WHAT is being DONE
- PascalCase
- Avoid underscores
- some implementations use underscores to denote private fields
- _carType
- Classes should be well defined
- One class per code file
- add properties above methods
- Done have large classes
Constructors
- Method ran when class is created
- Default constructor(not required)
public classname() {}
- Can overload with many constructor
public classname(string s1) {}
public classname(string s1, string s2) {}
public classname(int i1) {}
Constructor chaining
appending “: this()” to the overloaded constuctor method, will cause the default constructor to be called 1st, then the overloaded constructor
public classname(int i2) : this() {}
TestMethod Structure
Use 3 sections in the test
//Arrange var currentCar = NewCar(“Honda”); var expected = “Honda”; //Act string result = currentCar.ActorName; //Assert Assert.AreEqual(expected, result);
Namespaces
- Separates Classes to organize logic & avoid method name collisions
- Don't have namepace same as classname
- Ctrl+R, Gtrl+G
- <Company>.<Technology>.<Feature>
- PascalCasing
- avoid 'system'
- avoid using same classname in a namespace
Class org
- constructors
- properties
- methods
Static Classes
- Subject.Common
- Good for utilities
- use sparingly
- Don't use for random function bucket
- all classes should have a purpose & methods to support that purpose, so the need for static classes should be minimal
- push static methods into the classes for which that are used for
Caution!
- can't inherit them
- can't implement an interface
- can't have parameterized constructors
Singleton
- Class for which there is only ONE
- Good implementation has it as:
- Main Class is not static
- Class constuctor checks for any instance of the class,
- then returns the class if none exists
Method Overloading
- Same name, different signatures
- parameters must be different type or count
- return type is ignored for determining which method is called
Method Chaining
Constants vs Read-Only Fields
- Read-Only can assigned in constructor
- If an object is instantiated, read-only can be updated for each instance
- Use all caps for PascalCasing?
Properties
- A member that provides a flexible mechanism to private fields:
- Read
- Write
- Computes its value
- They are a safety mechanism to provide access to data
- Get/Set
- Lazy loading ( getter )
- Validate incoming value
Managing Objects Efficiently
<create examples>
Object needed once
- Create method to get/return the object
Object needed always
- get the object in the class constructor
- Assign a field?
Object needed sometimes
- Lazy Loading, if null, then return
Checking for null
int myInt = anObject?.intValue;
if(anObject!=null){}
use statement
- Good for DB & streaming connections
- good for FileStream operations, as it closes the streams when done
using(filestream){
}
References
- c-sharpcorner.com
- w3schools.com
- blog.sqlauthority.com
- stackoverflow.com
- dotnetrocks.com
- docs.microsoft.com
- Log in to post comments
Tags
