Eclipse Preferences Import/Export
- You can save the folder '.metadata' in your workspace.
- This folder contain your preferences, simply restore it after a re-installation and your done.
- The '.metadata' folder can contain projects/plugins specific settings, the 'core' eclipse settings are in: '.metadata/.plugins/org.eclipse.core.runtime/.settings'
- Theses 'core' settings can be exported using 'File -> Export -> Preferences'
Eclipse Essentials 2013
Environment Preparation
- JavaSE 6r29 JDK(and JRE): java.oracle.com
- Set Path & Test: “C:\Program Files\Java\jre6\bin”
- java -version
- javac -version
- IDE
- Eclipse: www.eclipse.org/downloads
- Eclipse IDE for Java Developers/Jave EE Developers
- Eclipse: www.eclipse.org/downloads
JARs(include in Eclipse project when needed):
- TestND: http://beust.com/eclipse
- Java Excel API: http://jexcelapi.sourceforge.net/
- JUnit: http://www.junit.org/
- Apache ANT (HTML reporting)
- Subversion http://subclipse.tigris.org/update_1.8.x
- Also check: http://download.eclipse.org/releases/juno/
Help and Tutorials
Java/Selenium Reading from Excel sheets:
- http://testerinyou.blogspot.com/2010/10/how-to-do-data-driven-testing-using.html
- http://functionaltestautomation.blogspot.com/2009/10/dataprovider-data-driven-testing-with.html
- http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ty3q2wQdPmU&feature=BFp&list=WL18EEBB0491EF4A05

Shortcuts:
CTRL-SPACE Code writing
CTRL + / Add/remove comments
CTRL + SHFT + O Organize imports (Add/remove imports)
ALT + UP/DOWN Move a line of code up or down
CTRL + D Delete Line
ALT+SHFT+J Element Comment

Starting Eclipse
Eclipse Start.bat: JDK7
This uses the JDK7 binaries:
|
set DEV_HOME=D:\DEVL\Java set JAVA_HOME=%DEV_HOME%\java32\jdk7 set PATH=%JAVA_HOME%\bin;%PATH%
start %DEV_HOME%\eclipse32\eclipse.exe -vm %JAVA_HOME%\bin\javaw.exe -showlocation -vmargs -server -Xms512m -Xmx1024m -XX:MaxPermSize=128m |
Eclipse.ini Configuration: JDK7
|
-startup plugins/org.eclipse.equinox.launcher_1.3.0.v20120522-1813.jar --launcher.library plugins/org.eclipse.equinox.launcher.win32.win32.x86_1.1.200.v20120522-1813 -product org.eclipse.epp.package.java.product --launcher.defaultAction openFile --launcher.XXMaxPermSize 256M -showsplash org.eclipse.platform --launcher.XXMaxPermSize 256m --launcher.defaultAction openFile -vm D:/DEVL/Java/java32/java32/jdk7/bin/javaw.exe -vmargs -Dosgi.requiredJavaVersion=1.5 -Dhelp.lucene.tokenizer=standard -Xms40m -Xmx512m |

HOME Environment Variable

Installing the Subversion Client
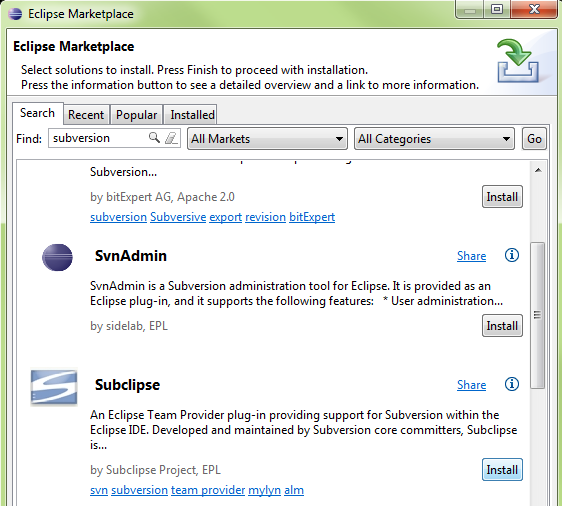
- Go to Help\Eclipse Marketplace and search by ‘Subversion’
- Select Subclipse and Install…
- http://subclipse.tigris.org/update_1.8.x
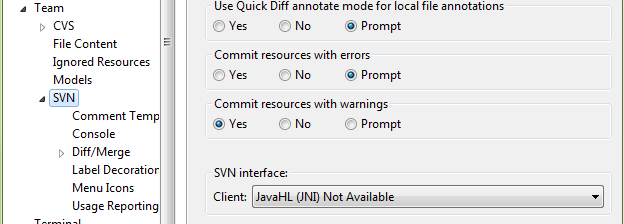
- Go to Preferences\Team\SVN
- The SVN interface should be JavaHL(JNI)
- Here it is Not Available
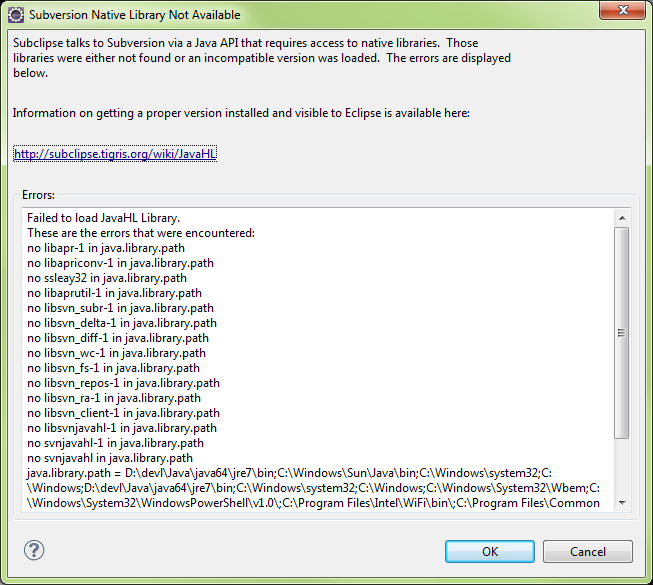
- If the Subclipse client plugins are missing, the following prompt will appear
Subclipse Library Not Available
Installing Subclipse from Help\New Software
- Go to Help\Install New Software…
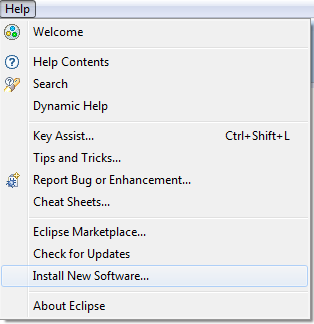
Locate “Subclipse – http://...”
Select Subclipse option, Click Next
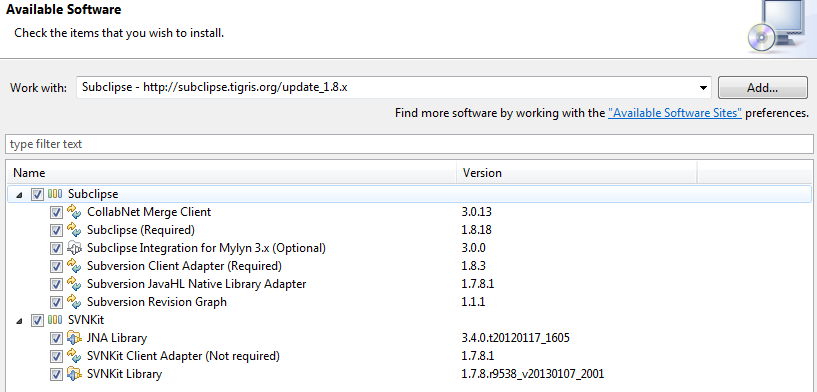
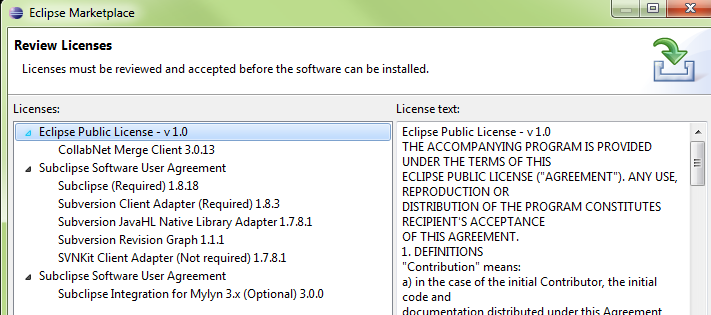
Acknowledge EULAs

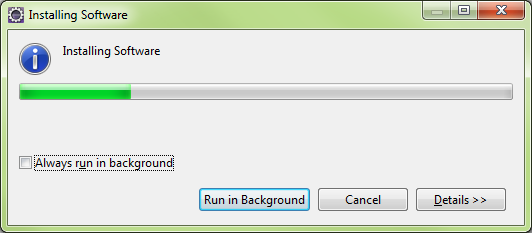
Eclipse will download selected packages
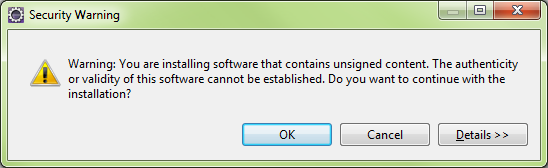
Security Warning
Eclipse will restart

Installing Subclipse From Help\Eclipse Market Place…
Eclipse Marketplace: Subclipse selection
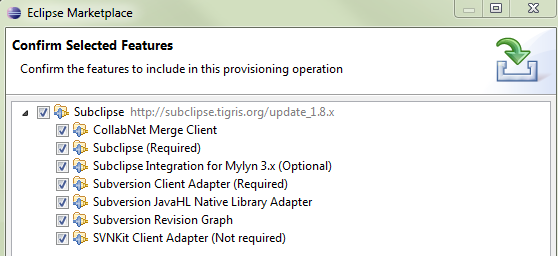
Select all packages
Acknowledge the EULAs
Eclipse will download the packages
Upon restarting, Eclipse will prompt for communicating Subclipse usage

Enabling the SVN Connector and Plugin
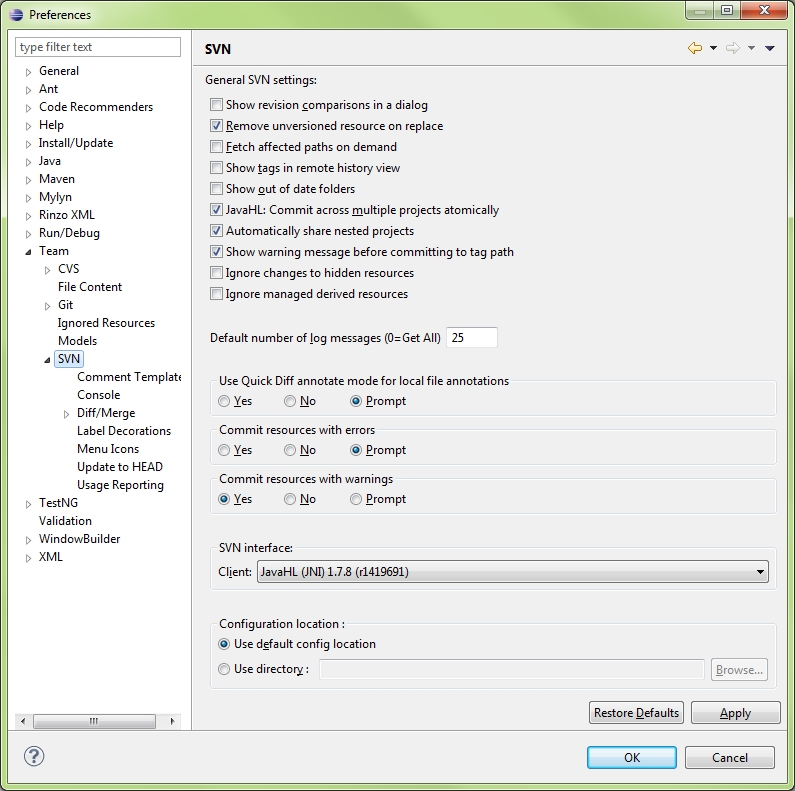
Eclipse\Preferences\Team\SVN
Select SVN interface: JavaHL and press OK
Open the SVN Repository View
The SVN repository Exporting Panel will appear

Right Click in the SVN repositories panel, select New..
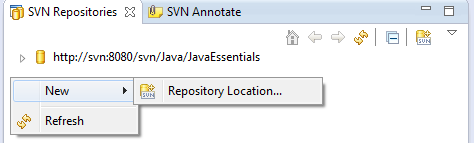
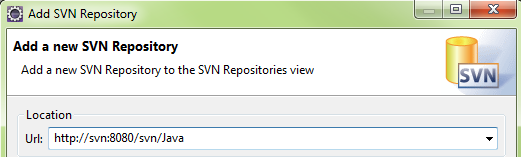
Enter the URL of the SVN Server and Repository
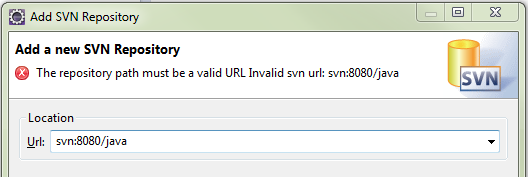
If Incorrect, Eclipse will indicate an Error
Accessing SVN from the Project Explorer

Eclipse About
About Main Form
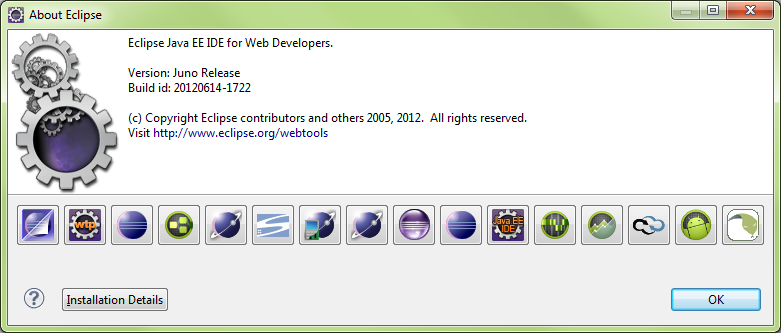
Installation Details
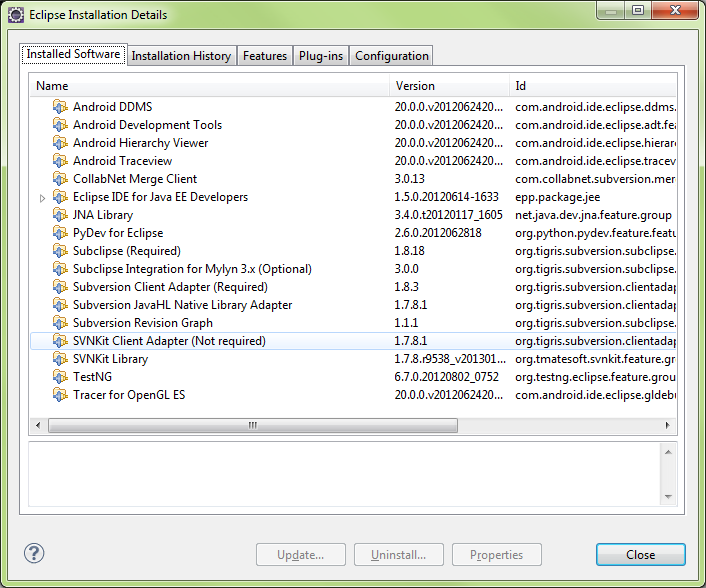
Installation History
Features
Plugins
Eclipse Installation Details

Eclipse Help

Main Contents View
Help Contents Expanded
Help Index
Help Search

Mylyn Task Manager
|
Mylyn is a Task-Focused Interface for Eclipse that reduces information overload and makes multi-tasking easy. It does this by making tasks a first class part of Eclipse, and integrating rich and offline editing for repositories such as Bugzilla, Trac, and JIRA. Once your tasks are integrated, Mylyn monitors your work activity to identify information relevant to the task-at-hand, and uses this task context to focus the Eclipse UI on the interesting information, hide the uninteresting, and automatically find what's related. This puts the information you need to get work done at your fingertips and improves productivity by reducing searching, scrolling, and navigation. By making task context explicit Mylyn also facilitates multitasking, planning, reusing past efforts, and sharing expertise. |
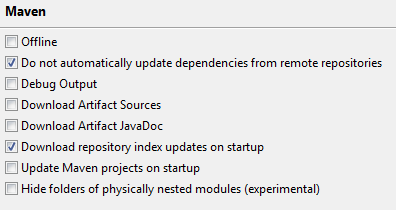
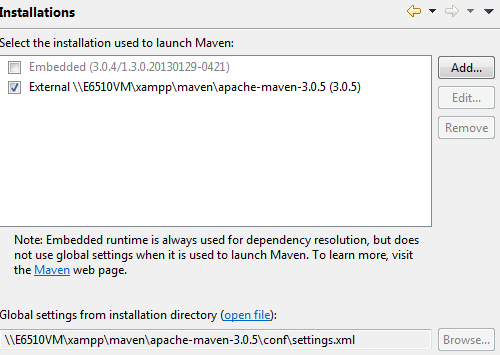
MAVEN
Eclipse M2E Installation
Searching repositories
Install Details
Review Licenses
Installing Software
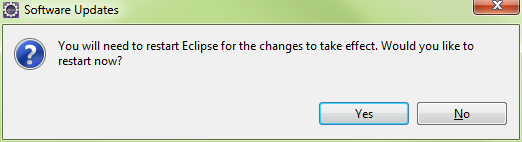
Restart
Eclipse Maven Configuration


Eclipse Development
Create Workspace
- Create WORKSPACE folder to contain PROJECTS
- New, Project....
- New, Class....(.java file is the class)
- Window > Prefrences > General > Appearance > Colors and Fonts.. > Text Font
- Run > Run Configurations... >
New Project
JRE Section
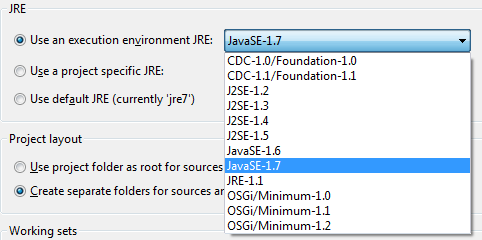
Configure JREs
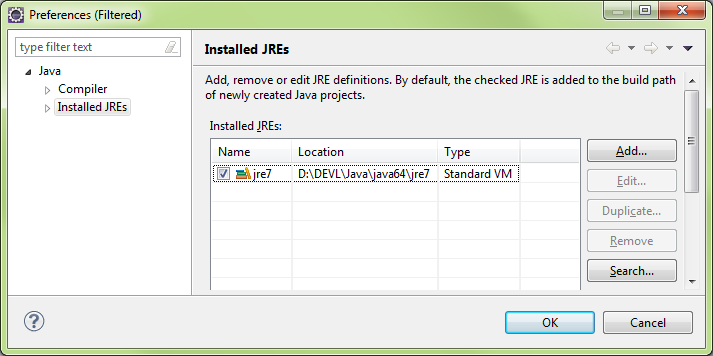
Configure Defaults
Import Projects
- File > Import > General > Existing Project into Workspace
- Exploded Project (Root Dir)
- Zipped Project (Archive File)
- Root Dir, OK
- Eclipse will autodetect projects
- Copy projects into workspace
- Close projects that aren’t in use (Right-Click, Close Project)
- Projects remain in workspace, just not open
Missing Dependencies and References
When opening a project, several errors can occur, such as missing depencies or references.
In this case, there is a missing JAR file
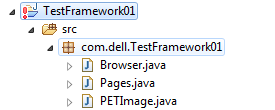
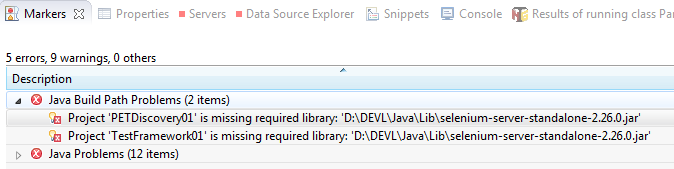
Right-click the error and select properties for more detailed look
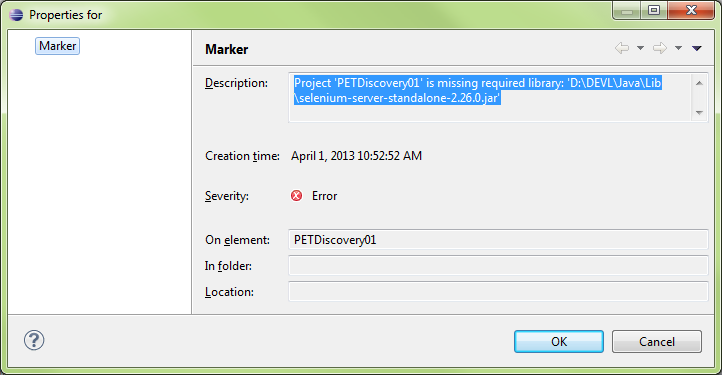
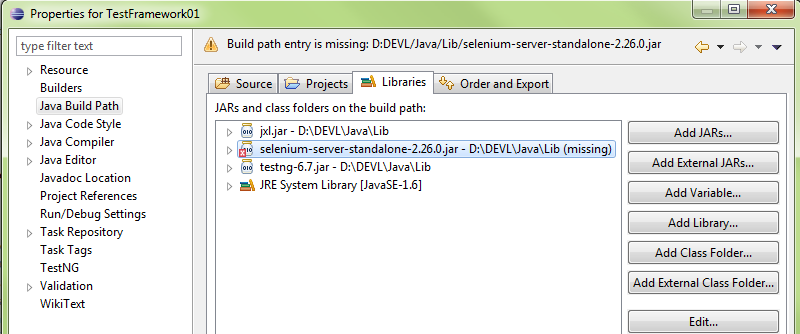
Right-click the project and select properties or press ALT-ENTER to bring u the project properties
Select the missing package and press Edit to select a new path to the file
IDE Layout
HutuBBB
Views/Panels

Perspectives
- Arrangement of Views
- Custom Perspectives: Window > Save Perspective As....
Command Line
- Dir to PROJECT\SRC
- javac Main.java
- dir = Main.class
- java Main
- javac Main.java -d ..\bin
- \src\Main.class
- javac Main.java -verbose
Note: Access Denied Errors
If Access Denied error occurs, set folder permissions to Everyone and give Full Control access.
D:\Eclipse\Java\CommandLine\src>javac Main.java -d D:\Eclipse\Java\CommandLine\bin
Main.java:2: error while writing Main: D:\Eclipse\Java\CommandLine\bin\Main.class (Access is denied
public class Main {
^
ClassPath
Similar to the classic dynamic loading behavior, when executing Java programs, the Java Virtual Machine finds and loads classes lazily (it loads the bytecode of a class only when this class is first used). The classpath tells Java where to look in the filesystem for files defining these classes.
The virtual machine searches for and loads classes in this order:
- bootstrap classes: the classes that are fundamental to the Java Platform (comprising the public classes of the Java Class Library, and the private classes that are necessary for this library to be functional).
- extension classes: packages that are in the extension directory of the JRE or JDK, jre/lib/ext/
- user-defined packages and libraries
By default only the packages of the JDK standard API and extension packages are accessible without needing to set where to find them. The path for all user-defined packages and libraries must be set in the command-line (or in the Manifest associated with the Jar file containing the classes).
Setting the path through an environment variable
The environment variable named CLASSPATH may be alternatively used to set the classpath. For the above example, we could also use on Windows:
Sometimes you have to check the JAVA_HOME also, if it is pointing towards the right JDK version
set CLASSPATH=D:\myprogram
java org.mypackage.HelloWorld
Diagnose
Application programmers may want to find out/debug the current settings under which the application is running:
System.getProperty("java.class.path")

Compiling and Running
Java package statement implies the directory structure where it exists within the project.
Should be unique
- package com.lynda.javatraining;
- \src\com\lynda\javatraining\HelloWorld.java
When compiling, use javac in the project root:
- C:\JavaProjects\HelloWorld>javac com\lynda\javatraining\HelloWorld.java
- HelloWorld.class
- HelloWorld.java
When running, use package reference and filename without “.java” extension
- C:\JavaProjects\HellowWorld>java com.lynda.javatraining.HelloWorld
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
- Static: allows class to be called directly?
|
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
|

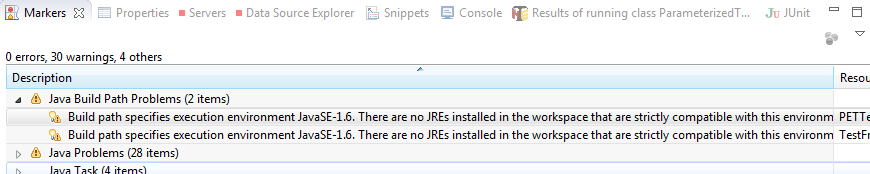
Project Errors
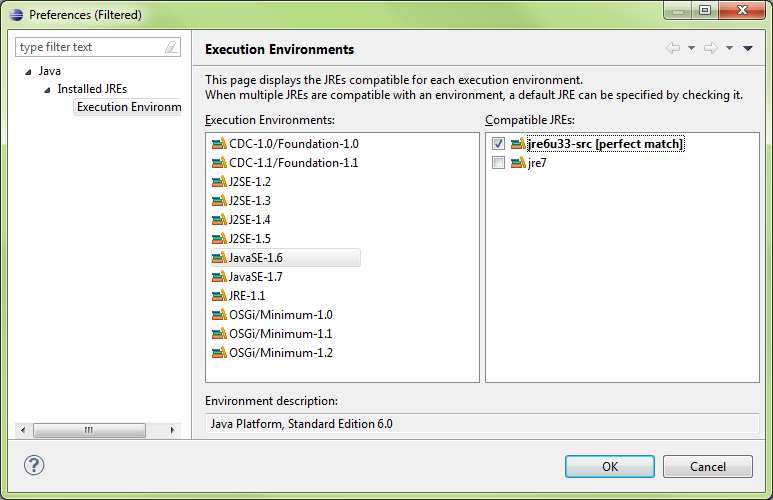
Error: Build Path specifics execution environment JavaSE1.6. There are no FREs installed in the workspace that are strictly compatible with the environment…
Fix: Add an additional JRE Library to the project and reference that in lieu of JRE7
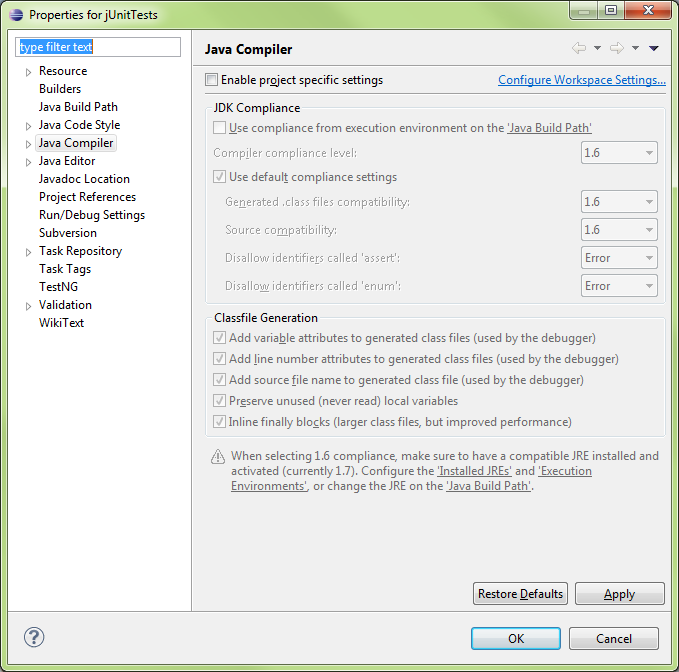
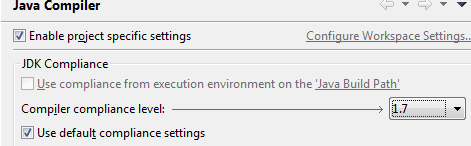
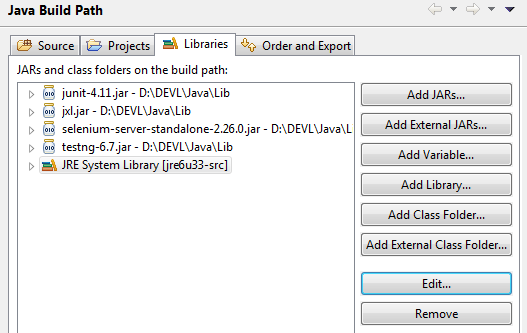
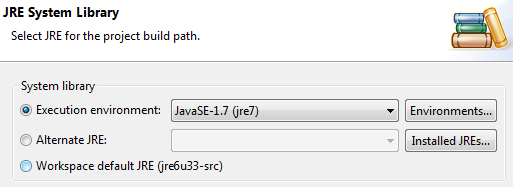
Press the Environments button to update the package refences
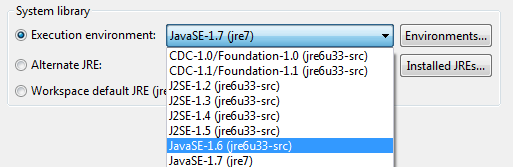
- IN this case, JavaSE-1.6 was mentioned in the error message so probably best to find a matching JRE for it
- jre6u33-src shows to be a [perfect match] for the requirement, so we’ll select it.

Java Language Tools
Main Class
public static void main(String[] args) {
Required by Class:
- public - can be called anywhere
- static - no instance required to run
- void - nothing returned by class
- String[] args
- [] - an array
- args - default variable to hold passed data
- Passed by Java’s JVM
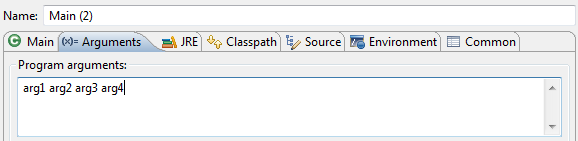
Passing Args
Command Line
java Main arg1 arg2
In Eclipse:

Switch Statements: Enums
Project > New > Enum

Code:
public enum Month {
JANUARY, FEBRUARY, MARCH; //Constants of enum class
}
public class SwitchWithEnums {
// Enumerations
public static void main(String[] args) {
// int month = 1;
Month month = Month.FEBRUARY;
switch(month) {
case JANUARY:
System.out.println("It's the first month");
break;
case FEBRUARY:
System.out.println("It's the second month");
break;
case MARCH:
System.out.println("Its the third month");
}
}
}

Methods
Refactoring
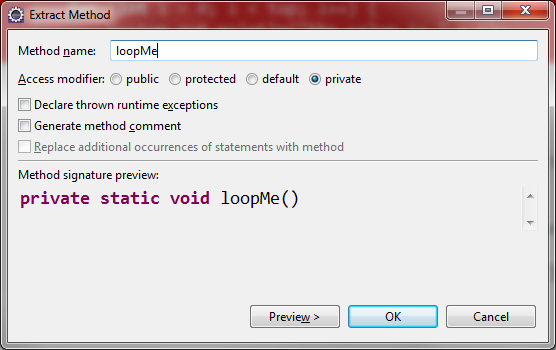
Code:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
doSomething();
//refactoring, copy code, Refactor..
//will create a new method and reference it here
loopMe();
}
private static void loopMe() {
int top = 10;
for (int i = 0; i < top; i++) {
System.out.println("the value is " + i);
}
}
//Access modifier public, private, protected (inheritance), none (protected package)
//Static - class method, only used inside class
//non-Static - used in instances
//Static must create instance to call non-Static '.method()'
private static void doSomething() {
System.out.println("This method has been called");
}
}

Extracting a Method
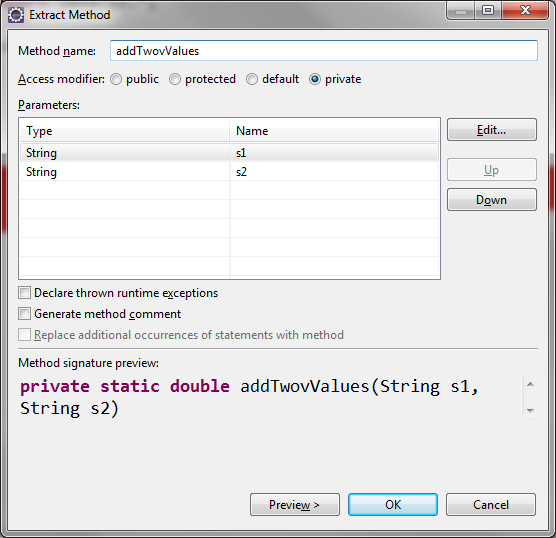
Code:
import java.io.*;
public class Calculator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = getInput("Enter a numeric value: ");
String s2 = getInput("Enter a numeric value: ");
// Extracting a Method
double result = addTwovValues(s1, s2);
System.out.println("The answer is " + result);
}
// Extracted Method
private static double addTwovValues(String s1, String s2) {
double d1 = Double.parseDouble(s1);
double d2 = Double.parseDouble(s2);
double result = d1 + d2;
return result;
}
private static String getInput(String prompt) {
BufferedReader stdin = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(System.in));
System.out.print(prompt);
System.out.flush();
try {
return stdin.readLine();
} catch (Exception e) {
return "Error: " + e.getMessage();
}
}
}

Extract Method with Error Handling
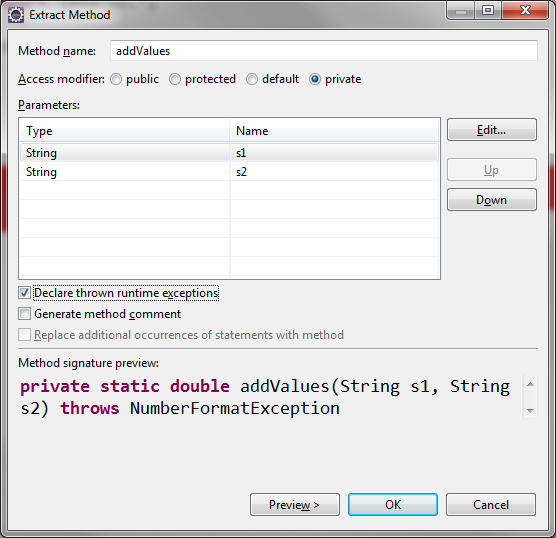

Extracting and Error Handling with Try/Catch Block: Revisited
String[] strings = {"Welcome!"};
System.out.println(strings[1]);
..
getArrayItem(); //refactored getArrayItem()
..
private static void getArrayItem()
throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException {
String[] strings = {"Welcome!"};
System.out.println(strings[1]);
}

try {
getArrayItem(); //refactored getArrayItem()
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
// e.printStackTrace(); // <--- throws ugly message
System.out.println("Array item was out of bounds");
}
Code:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Extrac Method with Error Handling
//Surround with try/catch blcok
try {
getArrayItem(); //refactored getArrayItem()
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
// e.printStackTrace(); // <--- throws ugly message
System.out.println("Array item was out of bounds");
//Array item was out of bounds
}
}
private static void getArrayItem()
throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException {
String[] strings = {"Welcome!"};
System.out.println(strings[1]);
}
}

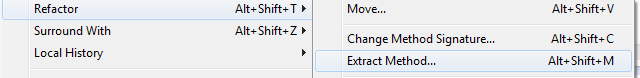
Debugger
Finding Possible Exceptions
Highlight command > Help > Dynamic Help > JavaDoc > CONSTRUCTOR > METHOD
URI uri = new URI("http:\\somecompany.com");
java.net.URISyntaxException: Illegal character in opaque part at index 5: http:\somecompany.com
at java.net.URI$Parser.fail(Unknown Source)
at java.net.URI$Parser.checkChars(Unknown Source)
at java.net.URI$Parser.parse(Unknown Source)
at java.net.URI.<init>(Unknown Source)
at Main.main(Main.java:10)
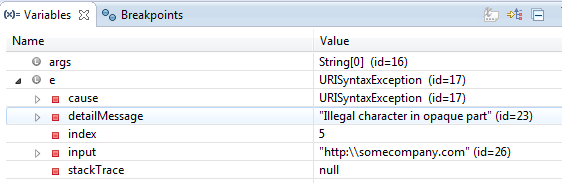
From e.printStackTrace();
To System.out.println(e.getMessage());
Code:
import java.net.URI;
import java.net.URISyntaxException;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Uniform Resource Identifier
try {
URI uri = new URI("http:\\somecompany.com");
} catch (URISyntaxException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
/*
e.printStackTrace();
java.net.URISyntaxException: Illegal character in opaque part at index 5: http:\somecompany.com
at java.net.URI$Parser.fail(Unknown Source)
at java.net.URI$Parser.checkChars(Unknown Source)
at java.net.URI$Parser.parse(Unknown Source)
at java.net.URI.<init>(Unknown Source)
at Main.main(Main.java:10)
*/
}
System.out.println("I'm alive!");
//Exception in thread "main" java.lang.Error: Unresolved compilation problem:
// Unhandled exception type URISyntaxException
// at Main.main(Main.java:8)
}
}

Classes
- Class = Filename.java
- Only one public class per java file
- Multiple classes only accessible within the files
- Refactoring is process of pulling code out, creating method/class
- Also changing class name is refactoring

Code:
From
result = divideValues(s1, s2);
To
result = SimpleMath.divideValues(s1, s2);
From
----------------------------------------------------------
public class Calculator2 {
private static double divideValues(String s1, String s2) {
double d1 = Double.parseDouble(s1);
double d2 = Double.parseDouble(s2);
double result = d1 / d2;
return result;
----------------------------------------------------------
To
----------------------------------------------------------
public class SimpleMath {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
public static double divideValues(String s1, String s2) {
double d1 = Double.parseDouble(s1);
double d2 = Double.parseDouble(s2);
double result = d1 / d2;
return result;
----------------------------------------------------------

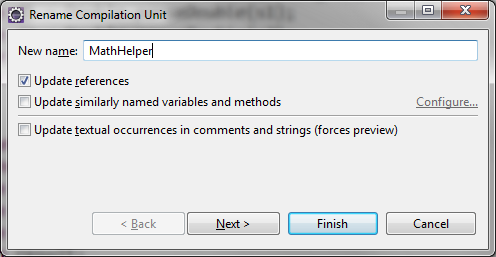
Packages
- If class is anywhere but default package, it must be declared
- when creating packages, use reverse domain...
- com.silosix.calc
Importing Packages
package com.lynda.calc;
import com.lynda.calc.helpers.InputHelper;
import com.lynda.calc.helpers.MathHelper;
same as:
package com.lynda.calc;
import com.lynda.calc.helpers.*;
CTRL-O will change * to specific class imports
Refactor > Move


Instance Methods
- Class method called from definition of the class
- building up utility functions that pass all data in the call
- STATIC present
- Instance method call from instance of the class - OBJECT
- objects stick around and retain their data so its always accessible.
- STATIC missing
- Method declarations
- static - class method
- public - called anywher ein ap
- private - only within class
- protected - only within this class or its subclasses
- Object Superclass methods with
- Olive()’s crush() method
- Olive inherits Object() methods/properties
Code: Main.java
package com.lynda.olivepress;
import com.lynda.olivepress.olives.Olive;
import com.lynda.olivepress.press.OlivePress;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//creating 3 anonymous Olive objects
Olive[] olives = {new Olive(), new Olive(), new Olive()};
OlivePress press = new OlivePress();
press.getOil(olives);
}
}
Code: OlivePress.java
package com.lynda.olivepress.press;
import com.lynda.olivepress.olives.Olive;
public class OlivePress {
public void getOil(Olive[] olives) {
for (Olive olive : olives) {
olive.crush();
}
}
}
Code: Olive.java
package com.lynda.olivepress.olives;
public class Olive {
public void crush() {
System.out.println("Ouch!");
}
}
Constructors
- Constructors have no return value (void, int, etc)
- can create multiple constructors (overloading) with different input specs
- Always create a ‘no argument’ constructor for clarity
- public OlivePress() { }
- Can Create a new constructor with fields....
Constructor of the Olive() class
public Olive() {
System.out.println("Constructor of " + this.name);
}
Creating another constructor to catch argument and populate a field:
public Olive(int oil) {
//this.oil means field(instance variable
//otherwise refers to argument
this.oil = oil;
}
Code:
package com.lynda.olivepress.olives;
public class Olive {
public String name = "Kalamata";
public String flavor = "Grassy";
public long color = 0x000000;
private int oil = 3;
//constructor, same name as class
//no return on constructors
//can overload the constructor
public Olive() {
System.out.println("Constructor of " + this.name);
}
public Olive(int oil) {
this.oil = oil;
}
public int crush() {
System.out.println("ouch!");
return oil;
}
}

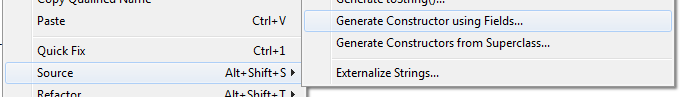
Getters/Setters
- OO development patters
- Fields should be private
- Get to data with get/set
- Create private get() and set()
Eclipse can create get/set code via Source:
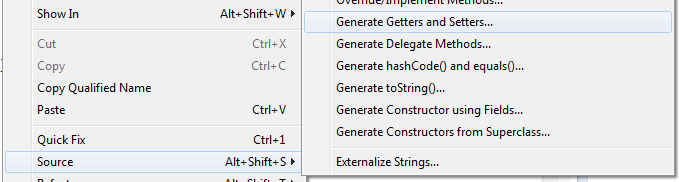
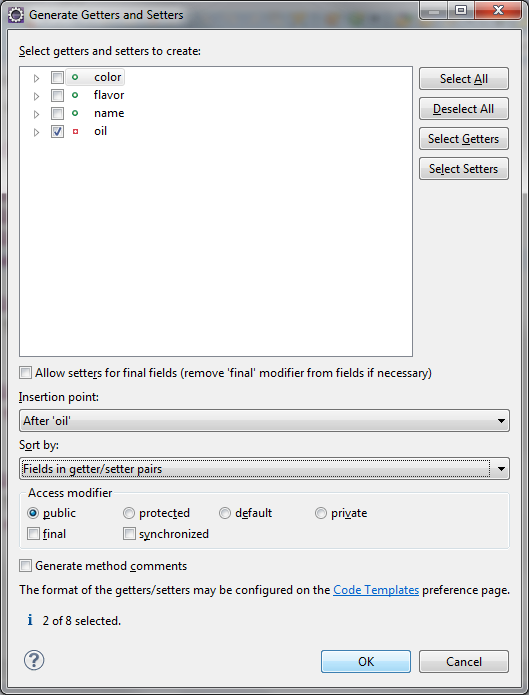
Creates:
public int getOil() {
return oil;
}
public void setOil(int oil) {
this.oil = oil;
}
Code: Main.java
package com.lynda.olivepress;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import com.lynda.olivepress.olives.Olive;
import com.lynda.olivepress.press.OlivePress;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Olive> olives = new ArrayList<Olive>();
Olive olive;
olive = new Olive(2);
System.out.println(olive.name);
olives.add(olive);
olive = new Olive(1);
System.out.println(olive.name);
olives.add(olive);
olive = new Olive(2);
System.out.println(olive.name);
olives.add(olive);
OlivePress press = new OlivePress();
press.getOil(olives);
System.out.println("You got " + press.getTotalOil() + " units of oil");
press.getOil(olives);
System.out.println("You got " + press.getTotalOil() + " units of oil");
}
}
Code: OlivePress.java
package com.lynda.olivepress;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import com.lynda.olivepress.olives.Olive;
import com.lynda.olivepress.press.OlivePress;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Olive> olives = new ArrayList<Olive>();
Olive olive;
olive = new Olive(2);
System.out.println(olive.name);
olives.add(olive);
olive = new Olive(1);
System.out.println(olive.name);
olives.add(olive);
olive = new Olive(2);
System.out.println(olive.name);
olives.add(olive);
OlivePress press = new OlivePress();
press.getOil(olives);
System.out.println("You got " + press.getTotalOil() + " units of oil");
press.getOil(olives);
System.out.println("You got " + press.getTotalOil() + " units of oil");
}
}
Code: Olive.java
package com.lynda.olivepress;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import com.lynda.olivepress.olives.Olive;
import com.lynda.olivepress.press.OlivePress;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Olive> olives = new ArrayList<Olive>();
Olive olive;
olive = new Olive(2);
System.out.println(olive.name);
olives.add(olive);
olive = new Olive(1);
System.out.println(olive.name);
olives.add(olive);
olive = new Olive(2);
System.out.println(olive.name);
olives.add(olive);
OlivePress press = new OlivePress();
press.getOil(olives);
System.out.println("You got " + press.getTotalOil() + " units of oil");
press.getOil(olives);
System.out.println("You got " + press.getTotalOil() + " units of oil");
}
}

Class Variables
- Java has no CONSTANT declaration so......
// public - accessible from entire app
// static - class var
// final - value can't be changed
IN Olive()...
public static final long BLACK= 0x000000;
using it
public long color = Olive.BLACK;

Inheritance
- Java has only single inheritance - only one inherited parent
- Parent/child
- Base/derived
- Superclass/subclass <- Preferred Java nomenclature
- By default Object() is the superclass unless directly specified
Polymorphism
- Can used as Superclass or Subclass
- Declare the object by Superclass
Superclass can have more than one subclass
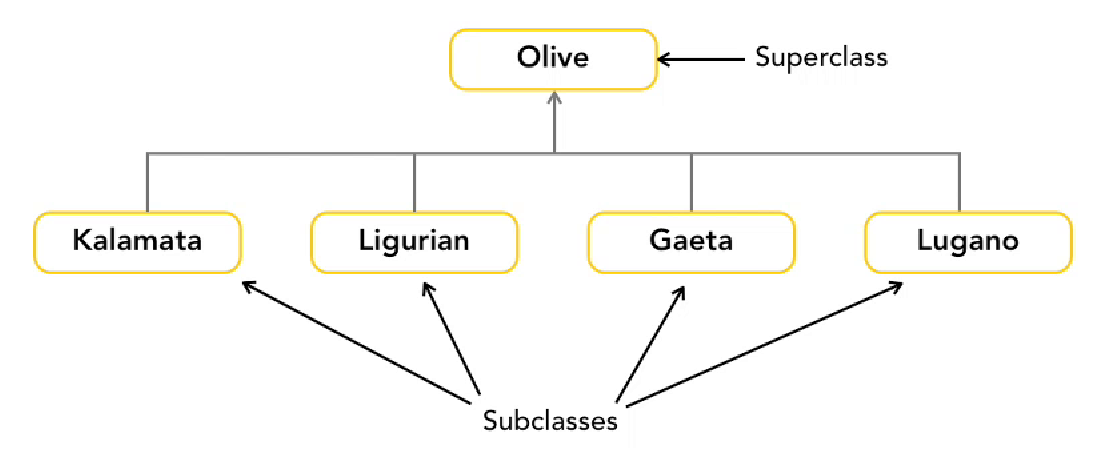
- Private - only called within own class
- Protected - called by own class or subclass
- Public - called from anywhere
Subclasses extend superclass
extending Olive by setting inital volume (setVolume)
public class Kalamata extends Olive() {
public Kalamata() {this.setVolume(2);}
}
public class Liguria extends Olive() {
public Liguria () {this.setVolume(5);}
}
…..this creates inheritance
Olive[] olives = {new Kalamata(), new Liguria(), new Kalamata()};
OlivePress press = new OlivePress(olives);
OliveOil oil - press.getOil;
Takes Kalamata() class and fits into Superclass Olive()
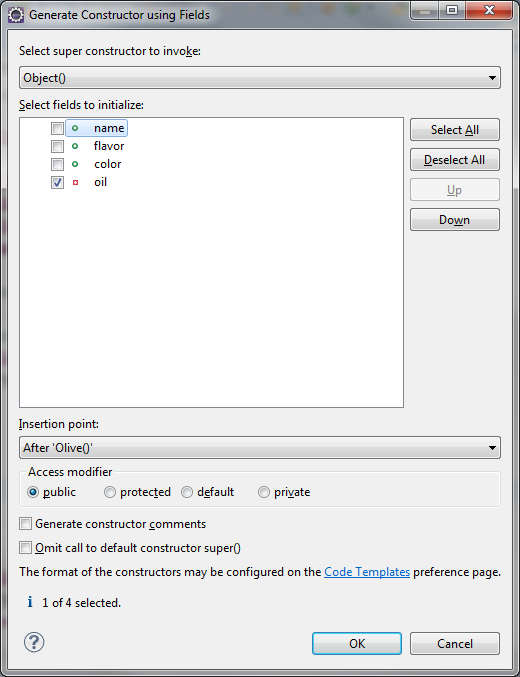
Extending Custom Classes
- Superclass doesnot pass on its constructor so...
- Each subclass needs its own constructor
In subclass... use IDE to copy constructors from the Superclass
Can select all or one...
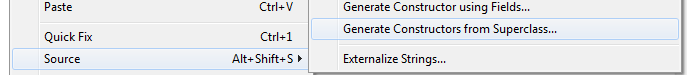
Superclass Olive() has two constructor methods (its overloaded)

Creates...
public Kalamata() {
super();//calling superclass constructor method
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
Code: Main
package com.lynda.olivepress;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import com.lynda.olivepress.olives.Kalamata;
import com.lynda.olivepress.olives.Ligurian;
import com.lynda.olivepress.olives.Olive;
import com.lynda.olivepress.press.OlivePress;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Olive> olives = new ArrayList<Olive>();
Olive olive;
//olive = new Olive(2); //Was calling SuperClass
olive = new Kalamata();
System.out.println(olive.name);
olives.add(olive);
olive = new Ligurian();
System.out.println(olive.name);
olives.add(olive);
olive = new Kalamata();
System.out.println(olive.name);
olives.add(olive);
OlivePress press = new OlivePress();
press.getOil(olives);
System.out.println("You got " + press.getTotalOil() +
" units of oil");
press.getOil(olives);
System.out.println("You got " + press.getTotalOil() +
" units of oil");
}
}
Code:Olive.java
package com.lynda.olivepress.olives;
public class Olive {
public static final long BLACK = 0x000000;
public static final long GREEN = 0x00ff00;
public String name = "Kalamata";
public String flavor = "Grassy";
public long color = Olive.BLACK;
private int oil = 3;
public int getOil() {
return oil;
}
public void setOil(int oil) {
this.oil = oil;
}
public Olive() {
System.out.println("Constructor of " + this.name);
}
public Olive(int oil) {
setOil(oil);
}
public int crush() {
System.out.println("ouch!");
return oil;
}
}
Code:Kalamata
package com.lynda.olivepress.olives;
public class Kalamata extends Olive {
public Kalamata() {
super(2); //calling superclass constructor method and passing '2'
this.name = "Kalamata";
this.flavor = "Grassy";
this.color = Olive.BLACK;
}
}

Overriding Methods (super.something();)
Code: Olive.java
package com.lynda.olivepress.olives;
public class Olive {
public static final long BLACK = 0x000000;
public static final long GREEN = 0x00FF00;
public String name = "Kalamata";
public String flavor = "Grassy";
public long color = Olive.BLACK;
private int oil = 3;
public int getOil() {
return oil;
}
public void setOil(int oil) {
this.oil = oil;
}
public Olive() {
System.out.println("Constructor of " + this.name);
}
public Olive(int oil) {
setOil(oil);
}
public int crush() {
System.out.println("crush from superclass");
//System.out.println("ouch!");
return oil;
}
}
Code: Kalamata.java
package com.lynda.olivepress.olives;
public class Kalamata extends Olive {
public Kalamata() {
super(2);
this.name = "Kalamata";
this.flavor = "Grassy";
this.color = Olive.BLACK;
}
//Annotation wth @...data type MUST match (super.crush())
@Override
public int crush() {
System.out.println("crush from subclass");
return super.crush();
}
}

Casting Objects
- As in conversion...upward/downward (int -> long / long -> int)
- casting
- upcasting - subclass as superclass (SAFE)
- downcasting - superclass as subclass (RISKY)
//Downcasting - will cause compiler error
Kalamata olive1 =olives.get(0);
//Downcasting Excplicitly
Kalamata olive1 = (Kalamata)olives.get(0);
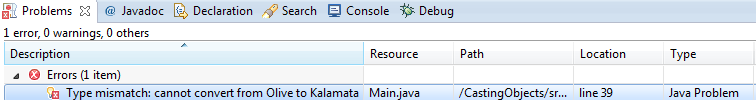
Create a Kalamata() olive1 from Olive() in ArrayList[0], position 0
Kalamata olive1 = olives.get(0);
Create a Kalamata() olive1 from Kalamata() Olive() in ArrayList[0], position 0
Kalamata olive1 = (Kalamata)olives.get(0);
Code:
Main.java
//Downcasting
Kalamata olive1 = (Kalamata)olives.get(0);
//downcast Olive() to (Kalamata)
//(Kalamata)olives.get(0) means USE SUBCLASS
System.out.println("Olive 1 is from " + olive1.getOrigin());
Kalamata.java (only in the Kalamata subclass, not others..)
getOrigin extends Olive()
public String getOrigin() {
return "Greece";
}

Interfaces
- Allows definition of classes’ structure
- final fields
- method names
- return data type
- Interfaces provides definition for creating classes
- Allows for polymorphism due to similarities
Code:
This method only accept ArrayLists (part of Collection data type I/F)
public void getOil(ArrayList<Olive> olives) {}
This is more flexible and can take any Data Type that implements the Collection I/F
public void getOil(Collection<Olive> olives) {

Creating Interfaces
- No constructor methods or other class elements
- Modeling behavior, not dynamic managment of data
- MUST BE PUBLIC
package com.lynda.olivepress.press;
public interface Press {
}
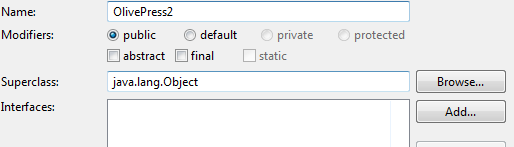
Creating a class with interface
Code:
package com.lynda.olivepress.press;
import java.util.Collection;
import com.lynda.olivepress.olives.Olive;
public class OlivePress2 implements Press {
@Override
public void getOil(Collection<Olive> olives) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
@Override
public int getTotalOil() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return 0;
}
@Override
public void setTotalOil(int totalOil) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
}

Creating JARs
- Build Project
- File > Export
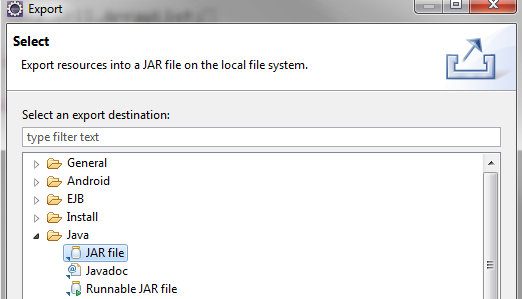
Don’t select Eclipse .classpath or .project
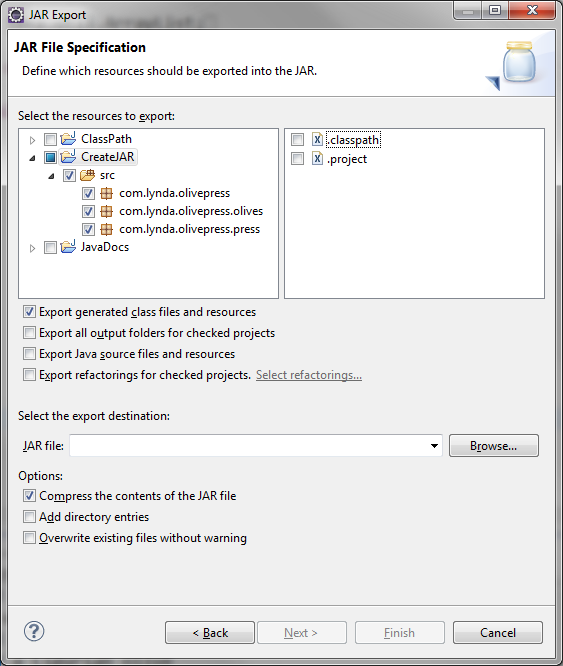
For Debugging...select these
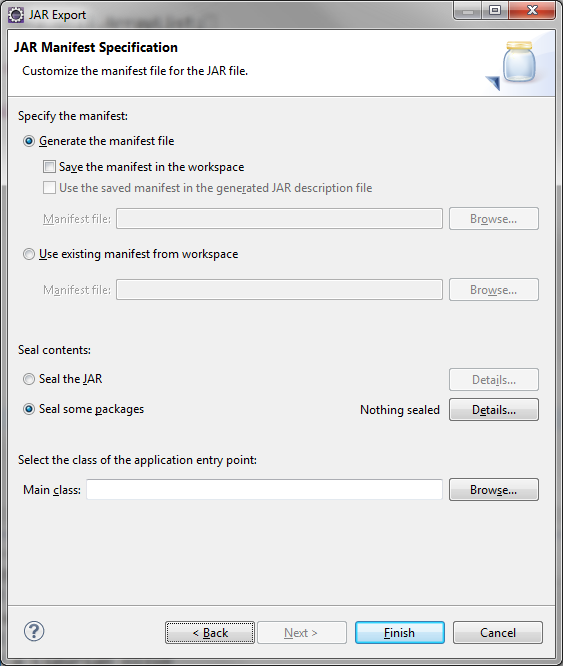
Manifest file has project metadata

ClassPath
Create a batch file and pass %1
set CLASSPATH=.
OR
For Linux
D:\TEMP\Eclipse>java -classpath .:OlivePressApp.jar com.lynda.olivepress.Main
For Windows
D:\TEMP\Eclipse>java -classpath .;OlivePressApp.jar com.lynda.olivepress.Main
You crushed a Kalamata olive
You crushed a Ligurian olive
You crushed a Kalamata olive
You have 5 units of oil
You crushed a Kalamata olive
You crushed a Ligurian olive
You crushed a Kalamata olive
Now you have 10 units of oil
Olive 1 is from Greece

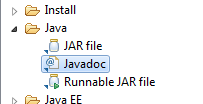
JavaDocs
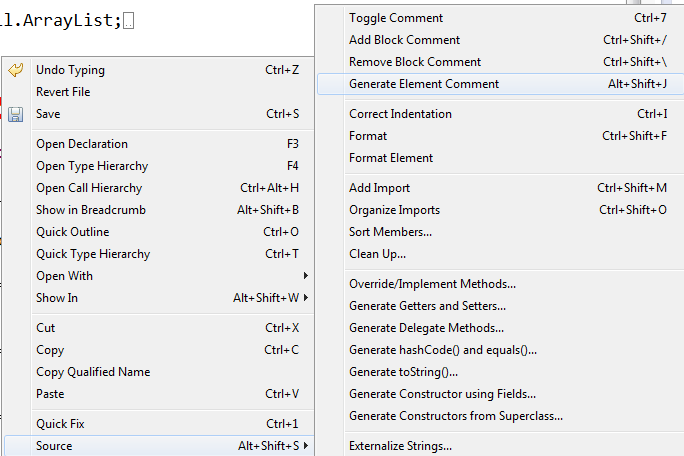
Source > Generate Element Comment
/**
* @author SiloSix
*
*/
File > Export > Java > JavaDoc
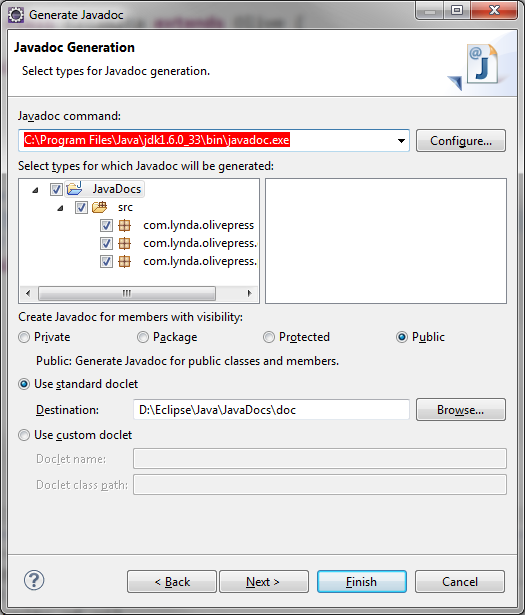
javadoc.exe: C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.6.0_33\bin\javadoc.exe
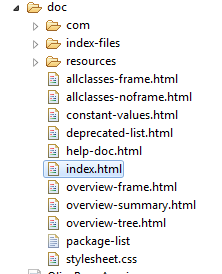

Resources
- apache commons
JUnit Class for testing:
- Annotations
- @Test, @Before, @After, @BeforeClass, @AfterClass, @Ignore
Code:
import static org.junit.Assert.*;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.AfterClass;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.BeforeClass;
import org.junit.Ignore;
import org.junit.Test;
public class myJUnit1 {
//No main() method, so JUnit will take over
@BeforeClass
public static void mBeforeTestClass(){
System.out.println("--------ClassBegin------------------");
}
//Annotation: Before EACH @Test
@Before
public void mBeforeTest(){
System.out.println("--------------------------");
}
//Gets executed every time we run the JUnit program
@Test
public void test1(){
if (mMultiply(10,30)==300) {
System.out.println("Multiply Pass");
} else {
System.out.println("Multiply Fail");
fail("Multiply Failed for 10 and 30");
}
}
//Test 2 code
@Test
public void test2(){
if (mAdd(10,30)==300){
System.out.println("Add Pass");
} else {
System.out.println("Add Fail");
fail("Add Failed for 10 and 30");
}
}
//Test 3 code
@Test
public void test3(){
if(mDivide(10,30)==300) {
System.out.println("Divide Pass");
} else {
System.out.println("Divide Fail");
fail("Divide Failed for 10 and 30");
}
}
//Test 4 code won't run due to @Ignore
@Ignore
@Test
public void test4(){
if(mDivide(10,30)==300) {
System.out.println("Divide Pass");
} else {
System.out.println("Divide Fail");
fail("Divide Failed for 10 and 30");
}
}
// Runs after EACH @Test
@After
public void mAfterTest(){
System.out.println("--------------------------");
}
@AfterClass
public static void mAfterTestClass(){
System.out.println("---------Class End-----------------");
}
//Multiply
public int mMultiply(int x, int y){
return x*y;
}
//Add
public int mAdd(int x, int y){
return x+y;
}
//Divide
public double mDivide(int x, int y){
return x/y;
}
}

Eclipse Web Services Project
Get Dependencies:
Axis2 Tools
Eclipse Java Web Developer Tools
Eclipse Web Developer Tools
Eclipse Java EE Developer Tools
JST Server Adapters
JST Server Adapters Extensions

Get Axis2 tools
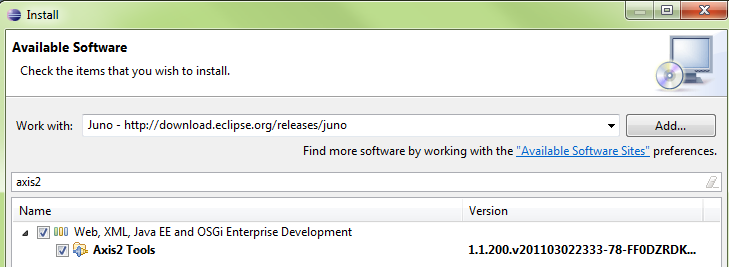
Get Eclipse Java Web Developer Tools
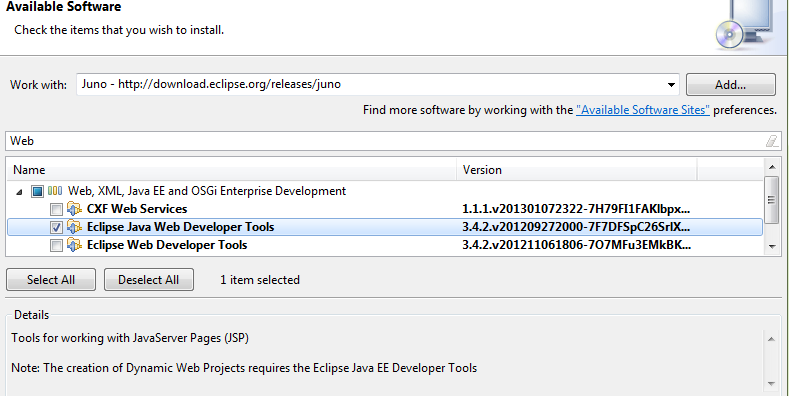
Get Eclipse Web Developer Tools
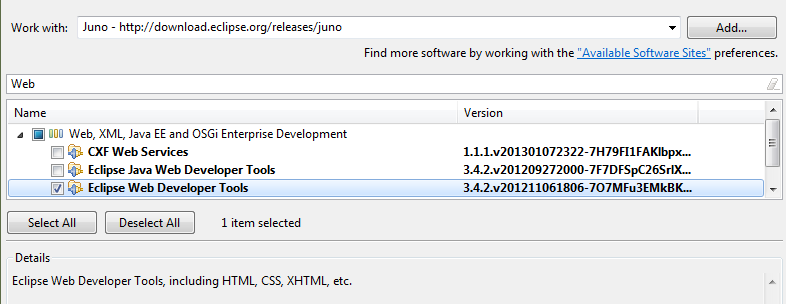
Get Eclipse Java EE Developer Tools
Get JST Server Adapters
Get JST Server Adapters Extensions
Get JAX-WS Tools

Create Web Service Server
Create Project (Server)
New\Dynamic Web Project
New Runtime…
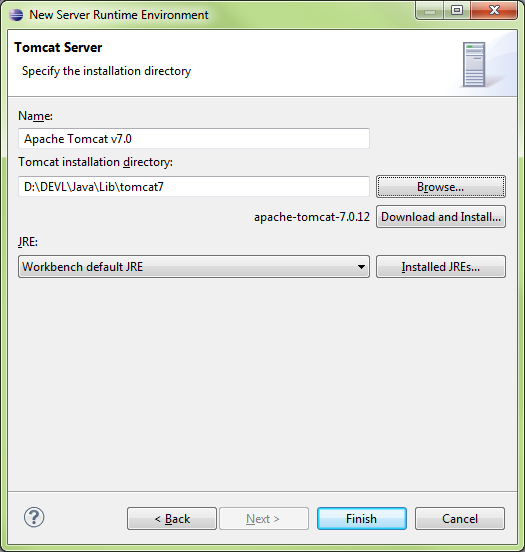
Configuration\Modify
Select Axis2 Web Services
Set Dynamic Web Module = 2.5
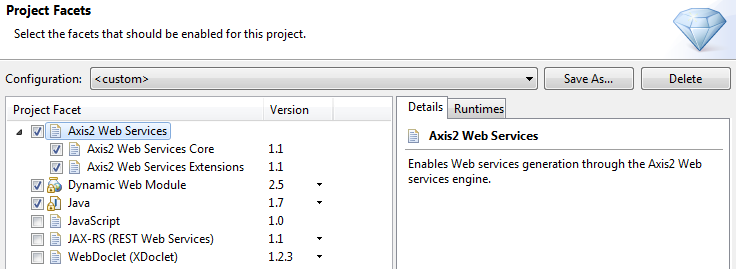
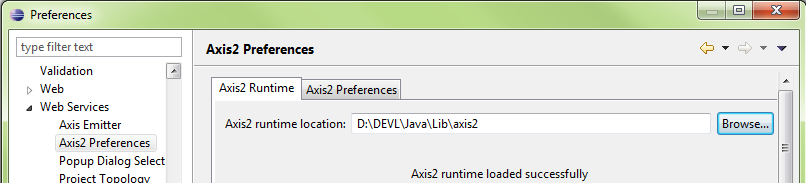
Configure Axis2 Web Services Core 1.1
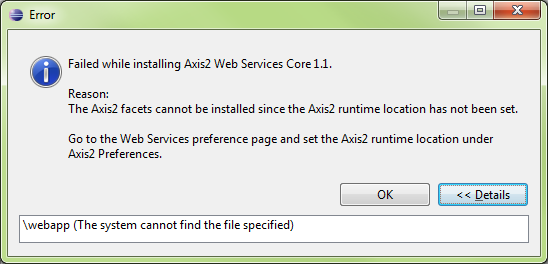
If this step isn’t performed, the following error message will be displayed when attempting to use the Axis2 Project Facet

Create Class (Server)
Add Class\OperatorClass
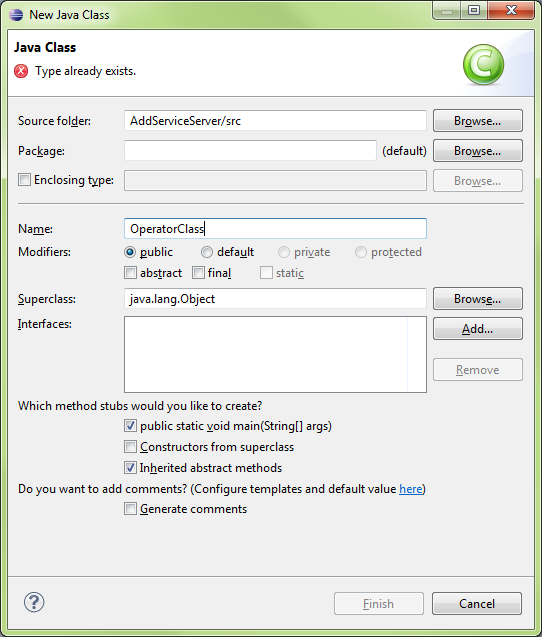
OperatorClass Code
|
public class OperatorClass {
public int Add(int a, int b){
return a+b;
} }
|

Create Service (Server)
New\Web Service
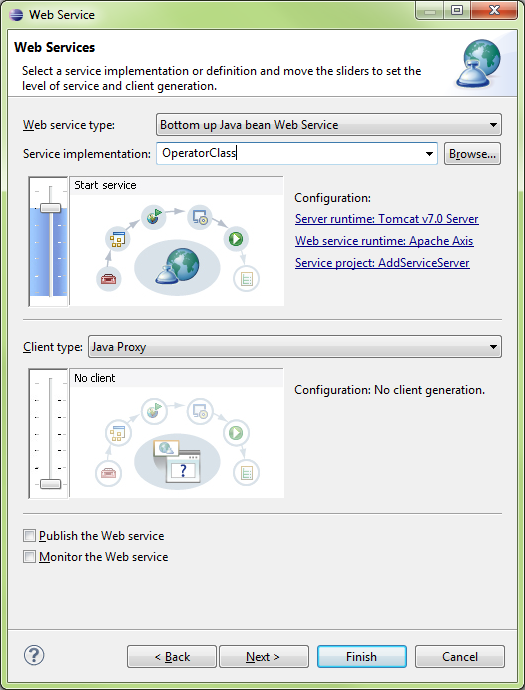
Run On Server\AddServiceServer (whole project)
Ensure Tomcat is running, then run
AddServiceServer successfully running on the server
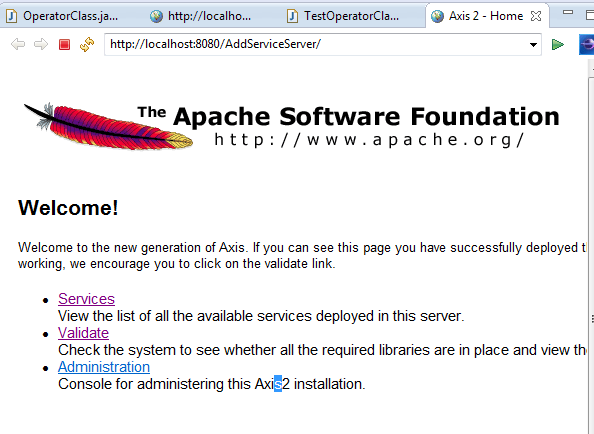
Click on Services\OperatorClass
The WSDL will be shown, copy link
http://localhost:8080/AddServiceServer/services/OperatorClass?wsdl
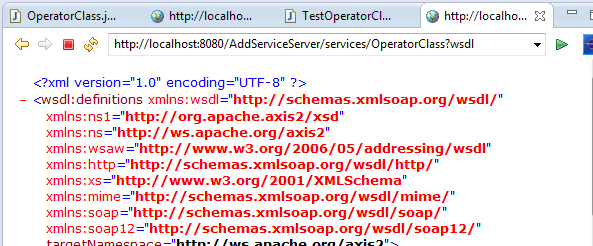
WSDL
|
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> - <wsdl:definitions xmlns:wsdl="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/wsdl/" xmlns:ns1="http://org.apache.axis2/xsd" xmlns:ns="http://ws.apache.org/axis2" xmlns:wsaw="http://www.w3.org/2006/05/addressing/wsdl" xmlns:http="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/wsdl/http/" xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" xmlns:mime="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/wsdl/mime/" xmlns:soap="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/wsdl/soap/" xmlns:soap12="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/wsdl/soap12/" targetNamespace="http://ws.apache.org/axis2"> <wsdl:documentation>Please Type your service description here</wsdl:documentation> - <wsdl:types> - <xs:schema attributeFormDefault="qualified" elementFormDefault="qualified" targetNamespace="http://ws.apache.org/axis2"> - <xs:element name="Add"> - <xs:complexType> - <xs:sequence> <xs:element minOccurs="0" name="a" type="xs:int" /> <xs:element minOccurs="0" name="b" type="xs:int" /> </xs:sequence> </xs:complexType> </xs:element> - <xs:element name="AddResponse"> - <xs:complexType> - <xs:sequence> <xs:element minOccurs="0" name="return" type="xs:int" /> </xs:sequence> </xs:complexType> </xs:element> </xs:schema> </wsdl:types> - <wsdl:message name="AddRequest"> <wsdl:part name="parameters" element="ns:Add" /> </wsdl:message> - <wsdl:message name="AddResponse"> <wsdl:part name="parameters" element="ns:AddResponse" /> </wsdl:message> - <wsdl:portType name="OperatorClassPortType"> - <wsdl:operation name="Add"> <wsdl:input message="ns:AddRequest" wsaw:Action="urn:Add" /> <wsdl:output message="ns:AddResponse" wsaw:Action="urn:AddResponse" /> </wsdl:operation> </wsdl:portType> - <wsdl:binding name="OperatorClassSoap11Binding" type="ns:OperatorClassPortType"> <soap:binding transport="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/http" style="document" /> - <wsdl:operation name="Add"> <soap:operation soapAction="urn:Add" style="document" /> - <wsdl:input> <soap:body use="literal" /> </wsdl:input> - <wsdl:output> <soap:body use="literal" /> </wsdl:output> </wsdl:operation> </wsdl:binding> - <wsdl:binding name="OperatorClassSoap12Binding" type="ns:OperatorClassPortType"> <soap12:binding transport="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/http" style="document" /> - <wsdl:operation name="Add"> <soap12:operation soapAction="urn:Add" style="document" /> - <wsdl:input> <soap12:body use="literal" /> </wsdl:input> - <wsdl:output> <soap12:body use="literal" /> </wsdl:output> </wsdl:operation> </wsdl:binding> - <wsdl:binding name="OperatorClassHttpBinding" type="ns:OperatorClassPortType"> <http:binding verb="POST" /> - <wsdl:operation name="Add"> <http:operation location="Add" /> - <wsdl:input> <mime:content type="application/xml" part="parameters" /> </wsdl:input> - <wsdl:output> <mime:content type="application/xml" part="parameters" /> </wsdl:output> </wsdl:operation> </wsdl:binding> - <wsdl:service name="OperatorClass"> - <wsdl:port name="OperatorClassHttpSoap11Endpoint" binding="ns:OperatorClassSoap11Binding"> <soap:address location="http://localhost:8080/AddServiceServer/services/OperatorClass.OperatorClassHttpSoap11Endpoint/" /> </wsdl:port> - <wsdl:port name="OperatorClassHttpSoap12Endpoint" binding="ns:OperatorClassSoap12Binding"> <soap12:address location="http://localhost:8080/AddServiceServer/services/OperatorClass.OperatorClassHttpSoap12Endpoint/" /> </wsdl:port> - <wsdl:port name="OperatorClassHttpEndpoint" binding="ns:OperatorClassHttpBinding"> <http:address location="http://localhost:8080/AddServiceServer/services/OperatorClass.OperatorClassHttpEndpoint/" /> </wsdl:port> </wsdl:service> </wsdl:definitions>
|

Create Web Service Client
Create Project (Client)
New\Dynamic Web Project
Java Settings
Web Module

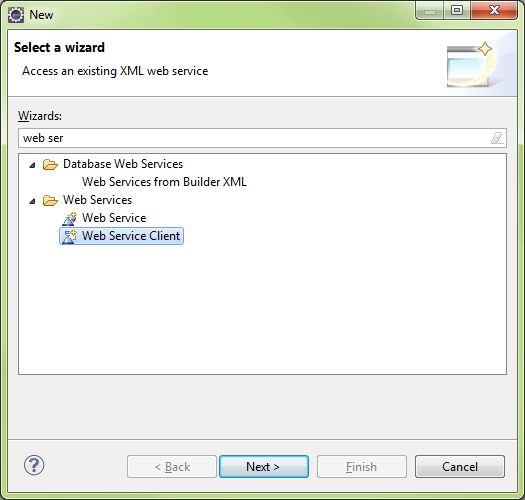
Create Service (Client)
New\Other…\Web Service Client
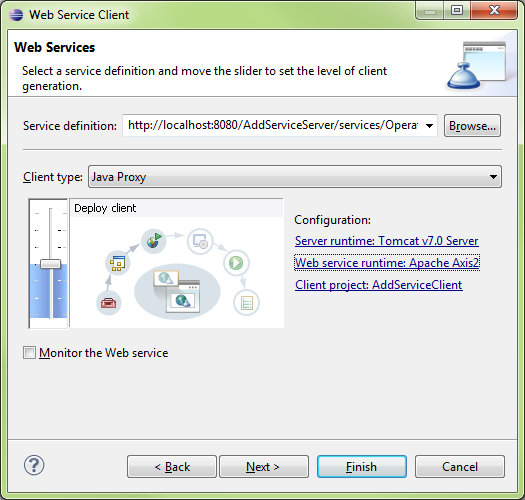
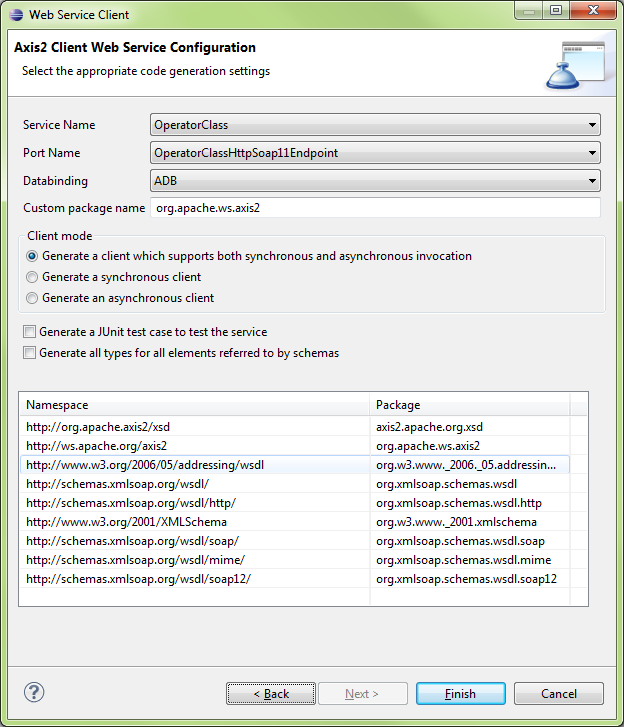

Create Class (Client)
Create New\Class
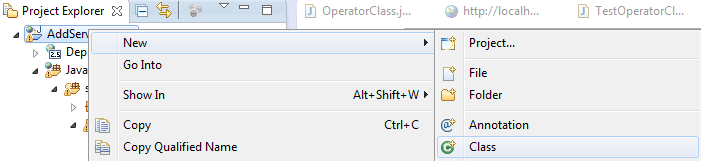
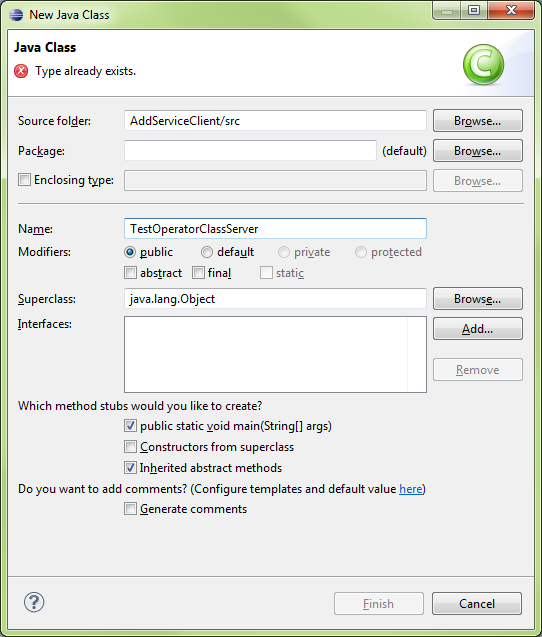
|
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
import org.apache.ws.axis2.OperatorClassStub; import org.apache.ws.axis2.OperatorClassStub.Add;
public class TestOperatorClassServer {
/** * @param args * @throws RemoteException */ public static void main(String[] args) throws RemoteException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub
OperatorClassStub classStub = new OperatorClassStub();
Add add0 = new Add();
add0.setA(8); add0.setB(9); int finalvalue = classStub.add(add0).get_return();
System.out.println(finalvalue); }
} |
Run the class
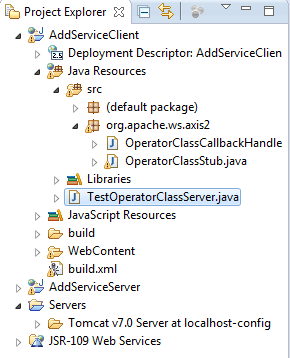

Installing Java and Eclipse on Ubuntu Linux: 2013 Updates
Do you have a JDK installed? You likely want to put $JDK_HOME/bin on your PATH, not the /bin of a JRE, as jar comes with JDK, not JRE.
Do this:
- Delete all installations of Java.
- Install the Java SDK (self-extracting) into /opt/jdk1.6.0_16 (for example)
- Create a symbolic link: ln -s /opt/jdk1.6.0_16 /opt/jdk
- Edit $HOME/.bashrc:
JAVA_HOME=/opt/jdk
PATH=$PATH:$HOME/bin:$JAVA_HOME/bin
- Logout and log back in.
This offers many advantages:
- You can install multiple versions of the SDK and need only switch a symbolic link.
- You know where all the files are located.
- You know exactly which version of Java is being used.
- No other versions are installed, so there cannot be any conflicts.
I have done this for years and have never had any problems with Java on Linux, except for packages that do not detect that Java is installed and attempt to install the OpenJDK.
Also, stay away from the OpenJDK as its fonts are terrible to behold.

EXTRAS

EXTRAS
Tutorial Glassfish Configuration
XXX
Web Services - Attempt1
New\Web\Dynamic Web Project
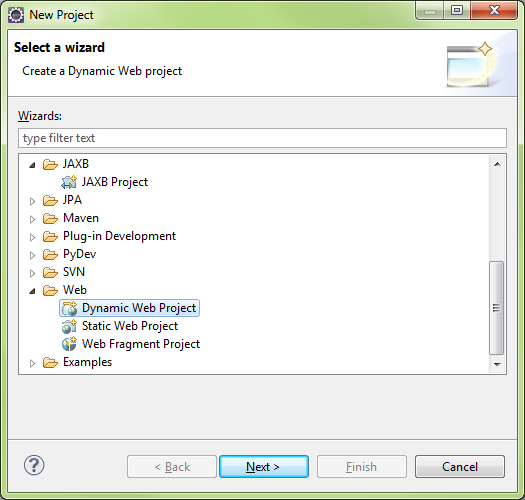
Select Tomcat v7
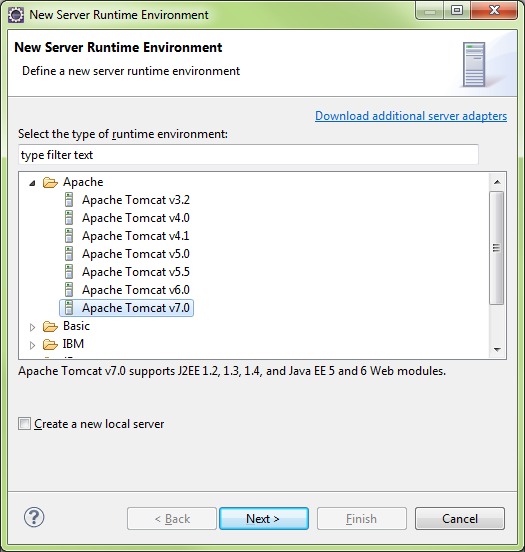
Browse for the Tomcat 7 Runtime on the Tomcat server, it needed Eclipse will download and install the runtime
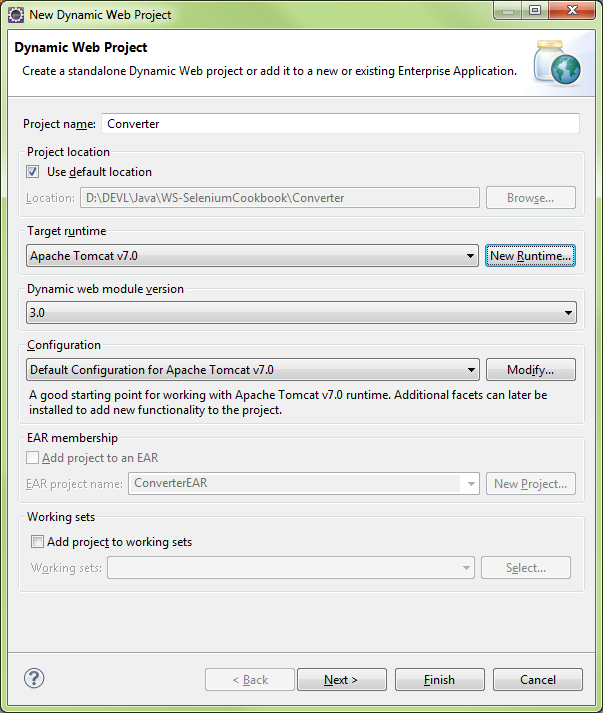
Modify Configuration
Tomcat7 default
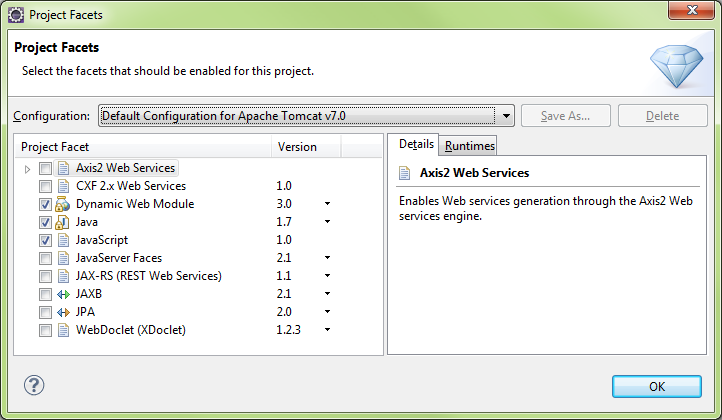
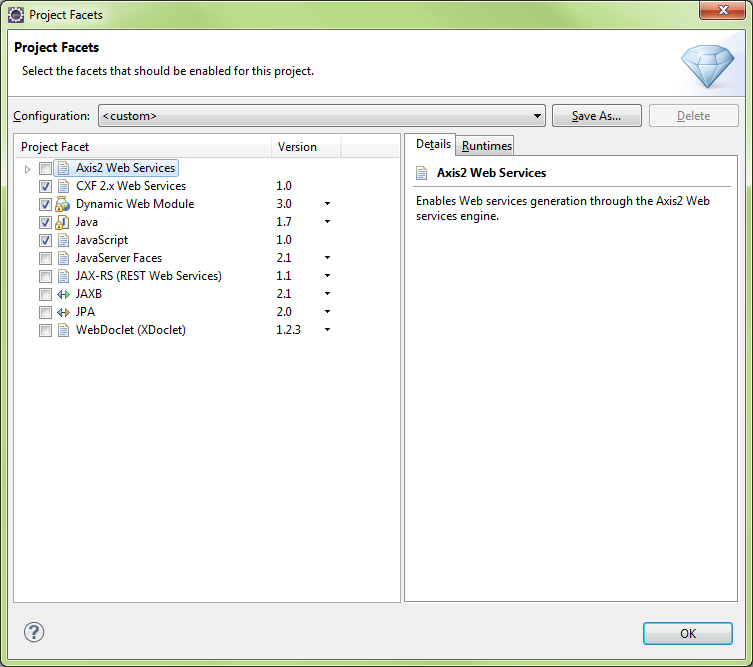
Add Axis2 Web Services
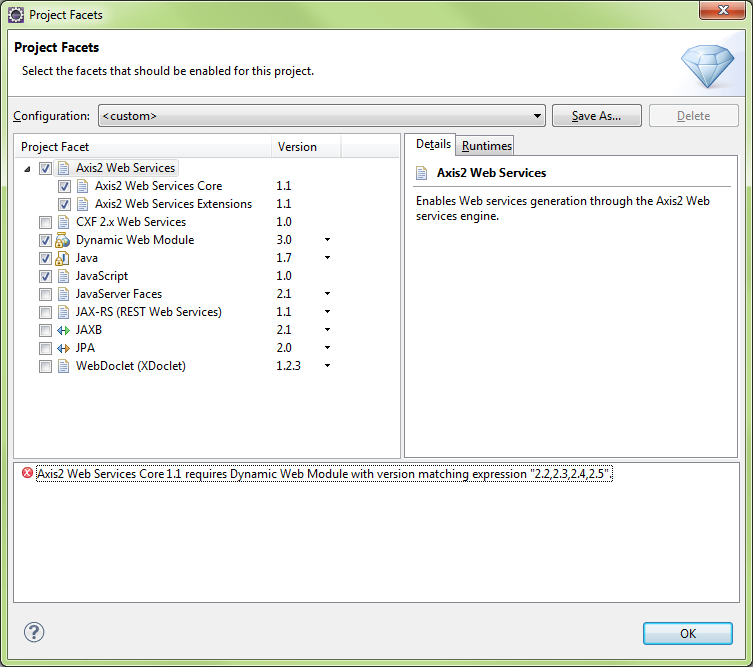
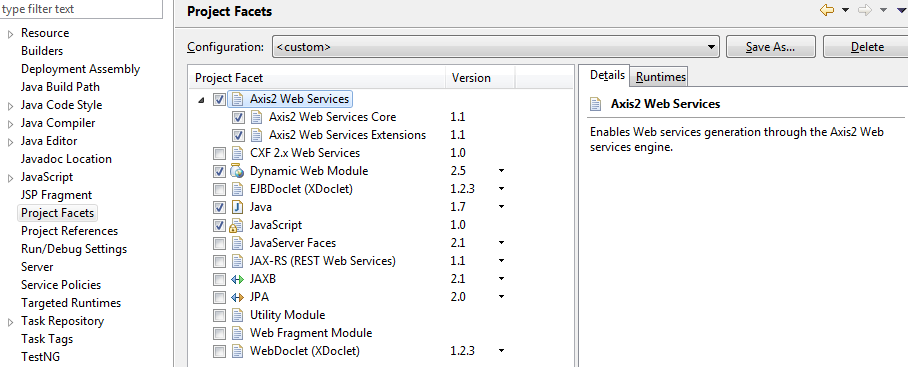
Need to select Dynamic Web Module v2.5 to clear above Axis2 error message
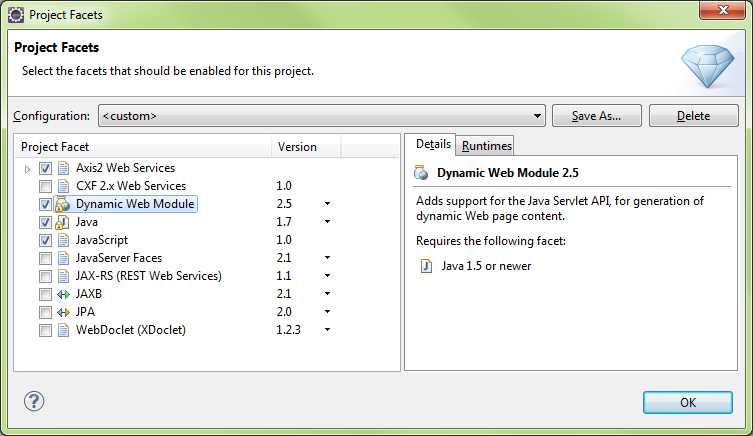
Need to add Axis2 Tools (v1.1.200.v201103…
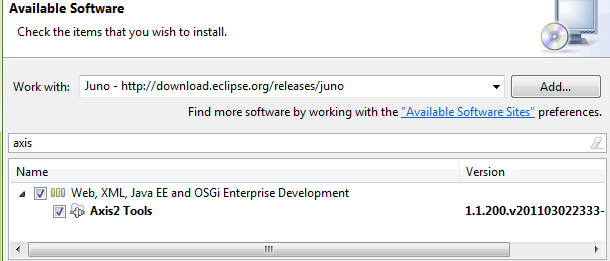
You can set Project facets after the fact via Project\Properties
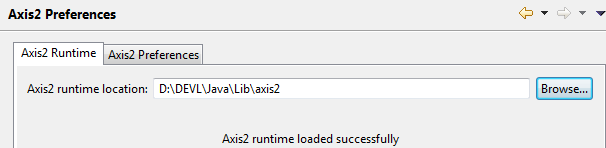
Download Apache Axis2 Binaries/Docs/War
http://axis.apache.org/axis2/java/core/download.cgi
Apache Axis2 ReleasesThis page provides links to the release versions of Axis2 Java. For more information, please see Apache Release FAQ. Different types of distributions are available for each released version:
1.6.x releasesThe following versions are available:
|
Create a Class
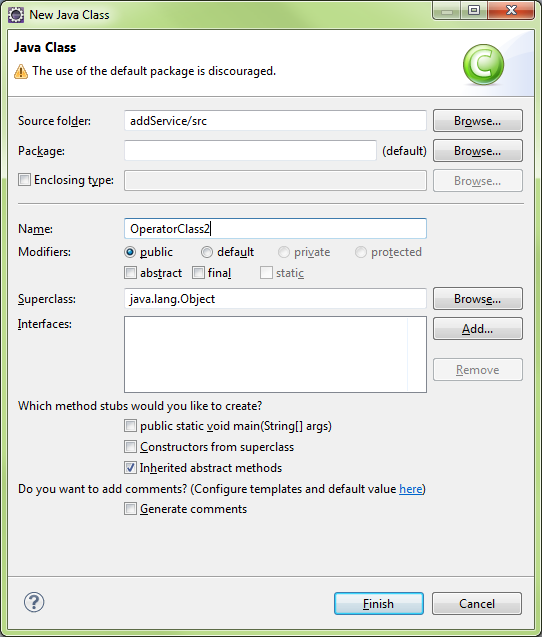
Run the Wizard for new WebService
Select Web Service Wizard

Click Browse and enter the class name to use for WebService
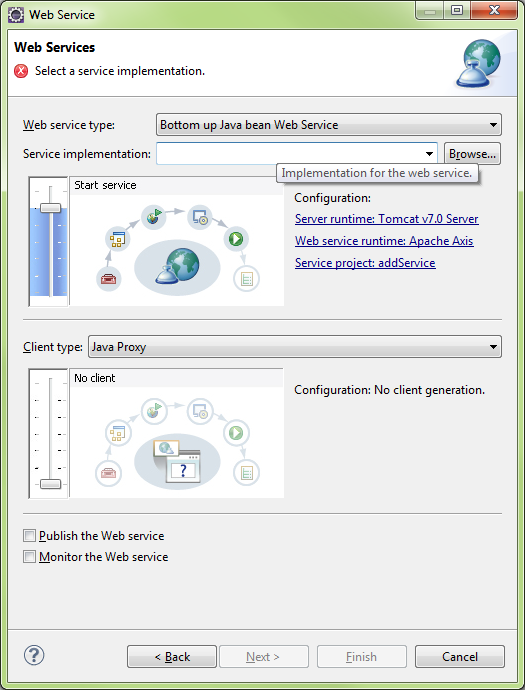
OperatorClass
Server Selection
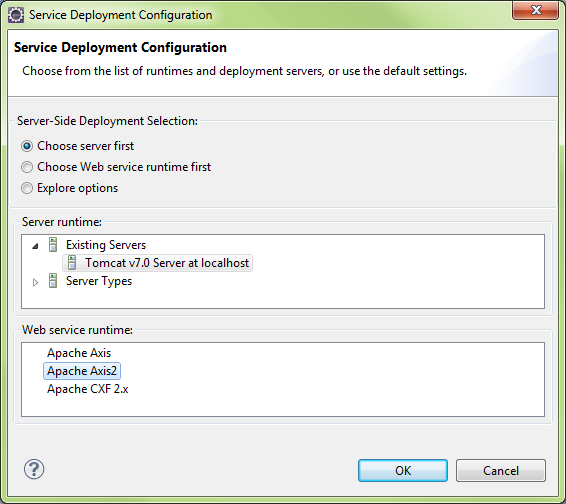
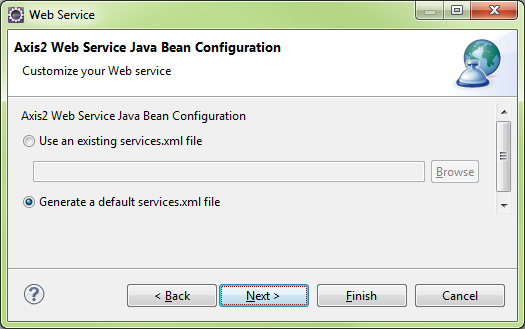
Generate a default services.xml file

Tomcat will start..
Run OperatorClass.java on the Tomcat Server..
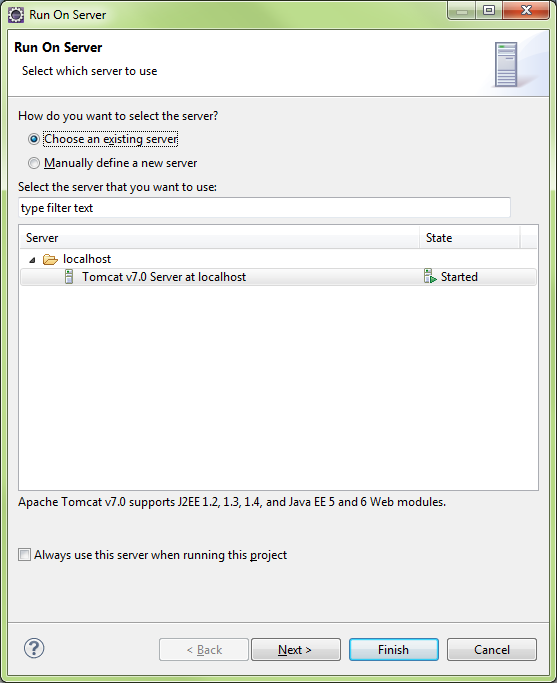
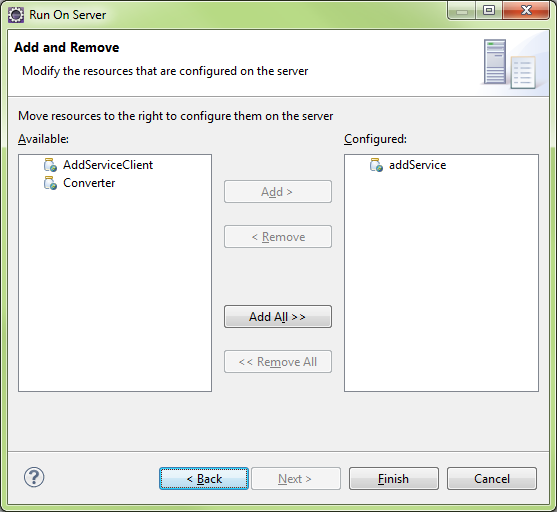
Create Web Service Client

Create Web Services Client

- Log in to post comments